
SCIA Arbitration Rules
(Adopted by the Second Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, effective as from February 21, 2019. Amended for the first time by the Second Council of SCIA at its fourteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from October 1, 2020. Amended for the second time by the Second Council of SCIA at its eighteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from February 21, 2022. Amended for the third time by the Third Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, such amendments shall take effect from October 1, 2024. Amended for the fourth time by the Third Council of SCIA at its thirteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from July 1, 2025.)
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Arbitration Rules
Article 1 Arbitration Institution
1. Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (also known as the South China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission, the Greater Bay Area International Arbitration Center, or the Shenzhen Arbitration Commission, formerly known as the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission South China Sub-commission and the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission Shenzhen Sub- commission; hereinafter the “SCIA”) is an arbitration institution established in Shenzhen, China.
2. Where all the parties to an arbitration agreement agree to submit their dispute to the SCIA for arbitration, or the name of the arbitration institution agreed by the parties is one of the former names of the SCIA, or it can be inferred that the SCIA is the arbitration institution, the parties shall submit their dispute to the SCIA for arbitration.
3. Where all the parties to an arbitration agreement agree to submit their dispute to the China (Shenzhen) Securities Arbitration Center, the China (Shenzhen) Intellectual Property Arbitration Center, the SCIA Maritime Arbitration Center, or any other branches established in mainland China of SCIA for arbitration, the arbitration case shall be accepted by SCIA.
Article 2 Jurisdiction
1. The SCIA accepts arbitration cases related to contractual disputes and other disputes over property rights and interests, including:
(a) international or foreign-related disputes;
(b) disputes related to the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, the Macao Special Administrative Region or Taiwan Region; and
(c) Chinese Mainland disputes.
2. The SCIA accepts arbitration cases related to investment disputes between states and nationals of other states.
Article 3 Scope of Application
1. Where the parties agree to submit their dispute to the SCIA for arbitration, unless otherwise agreed, the parties shall be deemed to have agreed to arbitration in accordance with the Arbitration Rules of the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (hereinafter “the Rules”).
2. Where the parties agree to refer their dispute to arbitration in accordance with the Rules or the special rules stipulated by the SCIA, they shall be deemed to have agreed to refer their dispute to arbitration by the SCIA.
3. Where the parties have agreed on the application of other arbitration rules or on a modification of the Rules, the parties’ agreement shall prevail unless such agreement cannot be implemented or is in conflict with a mandatory provision of the law applicable to arbitration proceedings. Where the parties have agreed on the application of other arbitration rules, the SCIA shall perform the relevant functions of the administrative authority under those arbitration rules.
4. Where the parties agree that dispute referred to under Article 2, Paragraph 1(a) or (b) of the Rules be governed by the “Arbitration Rules of the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law” (hereinafter, the “UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules”), the SCIA shall administrate the case in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules and the “SCIA Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the ‘UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules’” .
5. Where the parties submit their dispute referred to under Article 2, Paragraph 2 of the Rules to the SCIA for arbitration, the SCIA shall administer the case in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules and the “SCIAGuidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the ‘UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules’”.
6. Where there is any inconsistency between any special rules or guidelines stipulated by the SCIA and the Rules, the special rules or guidelines shall prevail. As to matters not covered in those special rules or guidelines, the relevant provisions in the Rules shall apply.
7. The SCIA or an arbitral tribunal shall have the power to resolve any matter not expressly stipulated in the Rules in a manner it deems appropriate.
Article 4 Place of Arbitration
1. Where the parties have agreed on the place of arbitration, the parties’ agreement shall prevail.
2. Where the parties have not agreed on the place of arbitration, the place of arbitration shall be the domicile of the SCIA. The SCIA may also determine the place of arbitration to be a location other than the domicile of the SCIA in regard of the circumstances of the case.
3. The arbitral award shall be deemed to be made at the place of arbitration.
Article 5 Language of Arbitration
1. Where the parties have agreed on the language of arbitration, their agreement shall prevail.
2. In the absence of such agreement, prior to the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the SCIA shall determine the initial language to be used in the arbitration proceedings, due regard being given to such relevant factors as the language of the contract involved. After the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the final language to be used in the arbitration proceedings shall be determined by the arbitral tribunal.
3. Where the parties have agreed to use more than one language, the arbitral tribunal may, upon obtaining consent from the parties, determine to adopt one language. If the parties fail to reach an agreement thereon, the arbitral proceedings may be conducted in multiple languages as agreed by the parties, in which case the resulting additional costs shall be borne by the parties.
4. Where a party or its representative or witness requires interpretation at an oral hearing, the party shall provide or request the SCIA to provide an interpreter(s).
5. The arbitral tribunal or the SCIA may, if it considers it necessary, require the parties to submit a corresponding translation or an abstract of the translation of their documents and evidentiary materials in the language(s) of the arbitration.
6. The arbitral award shall be made in the language(s) determined under the Paragraph 1, 2 or 3 of this Article.
Article 6 Service
1. Where the parties have agreed upon the means of service, such agreement shall prevail.
2. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, all written documents, notices and materials in relation to the arbitration proceedings may be delivered in person or sent by mail, facsimile, electronic mail, or any other means of electronic data interchange that can provide a record of delivery, or by any other means the SCIA considers appropriate.
3. Any arbitral document, notice or material sent by the SCIA to a party or its representativeshall be deemed to have been properly delivered if:
(a) delivered to the place of business, place of registration, place of residence, address indicated on household registration or on the identification card, address confirmed with the SCIA orally or in writing, any effective address for external use, address provided under the parties’ agreements or any other mailing address the SCIA considers appropriate;
(b) delivered to the addressee’s last known mailing address by post or by any other means that provides a record of delivery, if none of the foregoing addresses can be found after reasonable inquiries; or
(c) the subsequent arbitral documents, notices or materials are delivered to the original service address of the addressee if a party or its representative changes its address after having received the arbitral documents, notices or materials sent by the SCIA yet did not notify the SCIA of such change.
4. The time of delivery shall be the earliest time the document, notice or material reaches the addressee by any of the foregoing means of delivery.
5. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal may permit a party to directly send arbitral documents and evidentiary materials to the other party at the same time as the submission thereof to the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal, or to send them directly to the online arbitration platform of the SCIA, and then submit the record of delivery to the SCIA. The time of delivery will be determined by the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal according to the record of delivery.
Article 7 Bona Fide Cooperation
1. All the parties and their representatives shall proceed with the arbitration in bona fide and cooperative manner.
2. Where one party or its representative breaches the Rules, the agreements between the parties or the decisions of the arbitral tribunal such that the scheduled procedures are delayed or additional costs are incurred, the arbitral tribunal shall have the power to determine that such party shall bear the consequences therefrom.
3. All the parties and their representatives shall ensure the authenticity of their statements, submissions and documents, otherwise such party shall bear the consequences therefrom.
Article 8 Arbitration Agreements
1. An arbitration agreement means an arbitration clause in a contract or any other form of written agreement concluded between the parties providing for arbitration.
2. An arbitration agreement may be concluded between the parties either before or after the occurrence of the dispute.
3. An arbitration agreement shall be in writing, which includes but not limited to, a memorandum of contract, letter or electronic message (including telex, facsimile, electronic mail and electronic data interchange), etc. which is capable of expressing its contents in a tangible form.
4. It shall be deemed that there is an arbitration agreement in writing:
(a) where its existence is asserted by one party and not denied by
the other during the exchange of the Request for Arbitration and the Statement of Defence;
(b) where one party submits the dispute to the SCIA for arbitration and the other party expresses its agreement on arbitration in writing;
(c) where one party undertakes in writing to submit the dispute to the SCIA for arbitration and the other party submits the dispute to the SCIA for arbitration; or
(d) where the parties sign the record of oral hearings or other documents jointly during the arbitration proceedings, stating their agreement to arbitrate in the SCIA.
Article 9 Independence of Arbitration Agreements
An arbitration clause contained in a contract or an arbitration agreement attached to a contract shall be treated as independent and separate from all other clauses of the contract. The validity of an arbitration agreement shall not be affected by the non- existence,ineffectiveness, invalidity, expiry, rescission, modification, cancellation, suspension, termination, transfer, or impossibility of performance of the underlying contract.
Article 10 Objection to Jurisdiction and Decision on Jurisdiction
1. A party may raise its objection to jurisdiction over an arbitral case to the SCIA on grounds such as the nonexistence or invalidity of an arbitration agreement.
2. An objection to jurisdiction shall be raised in writing before the first oral hearing. Where a case is to be decided on the basis of documents only, such objection shall be raised in writing before the expiry of the time-limit for the submission of the first defence or within ten (10) days from the date of receipt of the notice for a document-based hearing. If a party fails to raise such objection, it shall be deemed to have agreed to the jurisdiction of the SCIA.
3. The SCIA or the arbitral tribunal authorised by the SCIA, shall have the power to decide on the jurisdiction. The arbitral tribunal may make its decision on jurisdiction either during the arbitration proceedings or in the arbitral award.
4. The arbitration shall proceed notwithstanding an objection to jurisdiction.
5. The SCIA or its authorised arbitral tribunal shall decide to dismiss the case upon finding that the SCIA has no jurisdiction. Where a case is to be dismissed before the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the decision shall be made by the SCIA. Where the case is to be dismissed after the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the decision shall be made by the arbitral tribunal.
Article 11 Request for Arbitration
1. A party applying for arbitration shall submit a Request for Arbitration.
2. The Request for Arbitration shall include:
(a) the names and addresses, telephone and facsimile numbers, electronic mail addresses and other contact details of the parties and of their representative(s);
(b) a reference to the arbitration agreement that is relied upon;
(c) the statement of claim;
(d) the facts and grounds on which the claim is based; and
(e) the signature and/or the seal affixed by the Claimant or its authorised representative(s).
3. Evidentiary materials in support of the claim and for the identification of the Claimant shall also be attached to the Request for Arbitration.
4. The arbitration proceedings shall commence on the day on which the SCIA receives the Request for Arbitration.
Article 12 Acceptance of a Case
After the Claimant submits a Request for Arbitration and its attachments, and makes advance payment of arbitration fees under Article 22 of the Rules, the SCIA shall accept the case if it finds the required formalities complete. Otherwise, the SCIA may request the Claimant to complete them within a specified time period. If the formalities remain incomplete upon the expiry of the specified time period, it shall be deemed that no request for arbitration has been made.
Article 13 Notice of Arbitration
After the SCIA accepts the Request for Arbitration, the SCIA shall send a Notice of Arbitration to the parties together with one copy of each of the Rules and the SCIA’s Panel of Arbitrators; the Request for Arbitration and its attachments submitted by the Claimant shall be forwarded to the Respondent simultaneously.
Article 14 Statement of Defence
1. The Respondent shall submit the Statement of Defence in writing within thirty (30) days from the date of receipt of the Notice of Arbitration.
2. The Statement of Defence shall include:
(a) the names and addresses, telephone and facsimile numbers, electronic mail addresses and other contact details of the Respondent and its representative(s);
(b) the defence, setting forth the facts and grounds on which the defence is based; and
(c) the signature and/or the seal affixed by the Respondent or its authorised representative(s).
3. Evidentiary materials in support of the defence and for the identification of the Respondent shall also be attached to the Statement of Defence.
4. Where the Respondent applies for an extension of time, if the arbitral tribunal deems any justified reasons exist, the arbitral tribunal may decide to grant an extension. Where the arbitral tribunal has not yet been formed, the decision on whether to grant the extension of the time period shall be made by the SCIA.
5. Failure by the Respondent to file a Statement of Defence or one that complies with the provisions of the Rules shall not affect the continuation of the arbitration proceedings.
Article 15 Counterclaim
1. The Respondent shall submit a counterclaim, if any, in writing within thirty (30) days from the date of receipt of the Notice of Arbitration. If the Respondent fails to submit a counterclaim within the above period, the decision on whether to accept the counterclaim shall be made by the SCIA before the formation of the arbitral tribunal or by the arbitral tribunal after it is formed.
2. The provisions of Articles 11-12 of the Rules shall apply mutatis mutandis to the submission and acceptance of a counterclaim.
3. The SCIA shall send a Notice of Acceptance of Counterclaim to the parties if it finds the required formalities for the counterclaim submitted by the Respondent complete.
4. The provision of Article 14 of the Rules shall apply mutatis mutandis to the defence of counterclaim by the Claimant.
Article 16 Amendments to the Claim or Counterclaim
1. Any party may apply in writing to amend its claim or counterclaim.
2. The decision to grant the application for such amendments shall be made by the SCIA before the formation of the arbitral tribunal or by the arbitral tribunal after it is formed. The SCIA or the arbitral tribunal has the power to reject such amendments if it considers that the amendments will delay the arbitration proceedings, be unfair to the other party or result in other circumstances that may not be appropriate for such amendments.
3. Amendments to the claim or the counterclaim shall not affect the conduct of the arbitration proceedings.
4. The provisions of Articles 11-14 of the Rules shall apply mutatis mutandis to the submission of, acceptance of, and defence to the amendments to the claim or counterclaim.
Article 17 Single Arbitration on Multiple Contracts
1. Claims arising from more than one contract, a principal contract and its subordinate contract(s), or a contract and its related contract(s) between the parties may be jointly made in a single arbitration, if it is agreed under all arbitration agreements of the such contracts to refer disputes to arbitration by the SCIA and the relevant disputes arise from the same transaction or a series of transactions.
2. Where an objection is raised by the Respondent, the decision shall be made by the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal authorised by the SCIA.
Article 18 Consolidation of Arbitrations
1. With the written consent by all parties, the SCIA may consolidate two or more pending arbitrations into a single arbitration to be decided by one arbitral tribunal.
2. Unless otherwise agreed by all the parties or otherwise determined by the SCIA, the arbitrations shall be consolidated into the arbitration that commenced first.
3. Following the consolidation of arbitrations, decisions on procedural matters shall be made by the SCIA before an arbitral tribunal is formed or by the arbitral tribunal after it is formed.
4. Where the arbitrations are consolidated, the arbitral tribunal shall have the discretion to either render a joint arbitral award on disputes between the parties, or render several arbitral awards separately.
Article 19 Concurrent Hearings
Where two or more arbitration cases involve the same or similar or related legal or factual issues and the arbitral tribunal is composed of the same arbitrators, the hearings may be held concurrently with the consent of the parties.
Article 20 Joinder of Additional Parties
1. Any party in a pending arbitration may apply in writing to join an additional party under the same arbitration agreement to the arbitration. The decision on whether to grant such joinder shall be made by the arbitral tribunal or, if it is not yet formed, by the SCIA.
2. Subject to the unanimous consent of the parties and the additional party, the additional party may apply in writing to join the arbitration proceedings. The decision on whether to accept such application shall be made by the arbitral tribunal or, if it is not yet formed, by the SCIA.
3. Where the SCIA has agreed to grant a joinder prior to the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the parties shall appoint arbitrators to form the arbitral tribunal in accordance with the provisions of Articles 28-31 of the Rules, with the time-limit stipulated therein be calculated from the date when the decision to grant the joinder is served. Where the SCIA has agreed to grant a joinder after the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the arbitral tribunal shall continue to hear the case. Any party that fails to participate in the formation of an arbitral tribunalshall be deemed to have waived such right, without prejudice to its right to challenge the arbitrators under Article 33 of the Rules.
Article 21 Claim between Multiple Parties
1. Where there are two or more Claimants or Respondents in a single arbitration, or an additional party is joined in the arbitration proceedings, any party can raise claims against any other party under the same arbitration agreement. The decision to accept such claims shall be made by the SCIA before an arbitral tribunal is formed, or by the arbitral tribunal after it is formed.
2. The provisions of Articles 11-16 shall apply mutatis mutandis to the submission and acceptance of, defence(s) to, and amendments of claims raised under this Article.
Article 22 Advance Payment of Arbitration Fees and Costs
1. A party making claims, counterclaims, or amendments to claims or counterclaims shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in advance within the required time-limit in accordance with the notice of the SCIA.
2. If a party requests for a set-off of any claim and such request requires the arbitral tribunal to consider additional matters, the request for set-off shall be regarded as an independent claim in terms of calculating the amount of arbitration fees and costs.
Article 23 Submission of Documents
Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal may require the parties to submit the Request for Arbitration, the Statement of Defence, the Statement of Counterclaim, the evidentiary documents, and other written documents through electronic means and/or as a hard copy.
Article 24 Representatives
A party may be represented by its authorised representative(s) including but not limited to the counsel from the Chinese Mainland or from jurisdictions outside the Chinese Mainland, in handling matters relating to the arbitration. In such a case, a Power of Attorney specifying the matters and scope of authorization shall be submitted to the SCIA.
Article 25 Preservation
1. A party may apply for preservation of property or to require the other party to perform or to refrain from performing a specific act before the commencement of or during the arbitration proceedings if, due to emergency, the legitimate interests of the party applying for preservation may suffer irreparable damages without an immediate preservation, or if the other party’s acts or some other circumstances may render the arbitral award impossible or difficult to be enforced.
2. A party may apply for preservation of evidence before the commencement of or during the arbitration proceedings, where it is likely that the evidence may be destroyed, lost, or become difficult to obtain later on.
3. If the place of arbitration is in Chinese Mainland, the party that applies for preservation before the commencement of the arbitration proceedings may directly submit the application to a competent court; if a party applies for preservation during the arbitration proceedings, the SCIA shall forward the application for preservation to a competent court. If the place of arbitration is in other countries or regions, the party that applies for preservation shall, according to the applicable laws, submit the application to a competent court or an arbitral tribunal for determination.
Article 26 Emergency Arbitrator
1. Where it is permissible under the applicable laws to the arbitration proceedings, a party who needs to apply for interim measure(s) due to any emergency may, during the time period between the commencement of the arbitration proceedings and the formation of the arbitral tribunal, submit a written application to the SCIA for the appointment of an emergency arbitrator. The decision on whether to grant such application for appointment shall be made by the SCIA.
2. The written applicationshall include:
(a) the names and addresses, telephone and facsimile numbers, electronic mail addresses and other contact details of the relevant parties and their representative(s);
(b) the interim measure(s) being sought and the grounds of the application; and
(c) opinions on the place, language, and applicable laws on the emergency arbitration proceedings.
3. If the SCIA determines that the emergency arbitration proceedings shall be commenced, the SCIA shall appoint an emergency arbitrator within two (2) days after receipt of both the application and the payment of fees required for the emergency arbitrator, and notify all the parties of such appointment. The SCIA shall forward the application documents and its attachments submitted by the applicant to the other party simultaneously.
4. The provisions of Articles 32-33 shall apply mutatis mutandis to the disclosure by and challenge to an emergency arbitrator. A party wishing to challenge the arbitrator on the basis of the matters disclosed by the arbitrator shall submit the challenge in writing within two (2) days after the written disclosure by the arbitrator is received. If a party fails to submit a challenge within the above time-limit, the party shall not subsequently challenge the arbitrator on the grounds of the matters disclosed by the arbitrator.
5. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the emergency arbitrator shall not act as an arbitrator for any such arbitration relating to the application of such interim measure(s).
6. The emergency arbitrator shall have the power to review the interim measure(s) applied for by any party in such a manner as the arbitrator considers appropriate, and ensure that each party shall have a reasonable opportunity to be heard.
7. The emergency arbitrator shall make the decisions with the grounds within fourteen (14) days from the date of appointment. The parties shall comply with such decisions made by the emergency arbitrator.
8. A party wishing to object to the decisions made by the emergency arbitrator may apply to the arbitrator for modification, suspension, or revocation of such decisions within three (3) days upon the receipt of such decisions. Whether to grant such application shall be decided by the arbitrator.
9. The arbitral tribunal, after being formed, may modify, suspend, or revoke the decisions made by the emergency arbitrator.
Article 27 Independence and Impartiality
Every arbitratorshall be and remain impartial and independent of the parties involved in the arbitration.
Article 28 Application of the Panel of Arbitrators
1. The parties shall appoint arbitrators from the Panel of Arbitrators of Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (hereinafter, the “Panel of Arbitrators”).
2. Where an arbitration is governed by the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules or the SCIA Rules of Maritime and Logistics Arbitration, the parties may either appoint arbitrator(s) from the Panel of Arbitrators or nominate arbitrator candidate(s) outside the Panel of Arbitrators . The candidate(s) so nominated may serve as arbitrator(s) after being confirmed by the SCIA.
Article 29 Number of Arbitrators and Composition of Arbitral Tribunal
1. The parties may reach an agreement on the number of arbitrators, which may be one (1) or three (3) persons.
2. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties or provided by the Rules, an arbitral tribunalshall be composed of three arbitrators.
3. Parties may agree on the means of appointing arbitrators, unless such agreement cannot be implemented or is in conflict with a mandatory provision of the law applicable to arbitration proceedings.
Article 30 Arbitral Tribunal of Three Arbitrators
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, within fifteen (15) days from the date of receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, the Claimant and the Respondent shall each appoint, or entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, an arbitrator, failing which, the arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA. Where there are two or more Claimants and/or Respondents in an arbitration, the Claimant side and/or the Respondent side shall each jointly appoint or jointly entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint one arbitrator, failing which, the arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
2. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, within fifteen (15) days from the date of the Respondent’s receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, the parties shall jointly appoint or jointly entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint the presiding arbitrator, failing which, the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA. Where any party expressly waives in writing the right to jointly appoint or jointly entrust the President to appoint the presiding arbitrator, the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA, not subject to the above time-limit.
3. In the alternative, the parties may agree, and the President of the SCIA may also decide that the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed jointly by the two appointed arbitrators under Paragraph 1 of this Article. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, where the two appointed arbitrators fail to appoint the presiding arbitrator within ten (10) days from the date of the appointment of the second arbitrator, the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
4. At the request of or with the consent of the parties, the President of the SCIA may recommend a list of more than three (3) candidates for the presiding arbitrator for each of the parties to rank in the order of their respective preference within five (5) days of receipt of the list. Out of the recommended candidates, a candidate placed in the highest ranking in the lists of both parties shall be deemed to be jointly appointed by both parties as the presiding arbitrator. If there is more than one candidate being placed in the highest ranking, the President of the SCIA shall choose one of them as the presiding arbitrator jointly appointed by the parties.
5. At the request of or with the consent of the parties, the President of the SCIA may recommend a list of more than three (3) candidates for the presiding arbitrator, from which each of the parties may choose one as its preferred presiding arbitrator within five (5) days of receipt of the list. Where a candidate is chosen by both parties, such candidate shall be deemed to have been jointly appointed by both parties as presiding arbitrator. If more than one candidate are chosen by both parties, the President of SCIA shall decide one of them as the presiding arbitrator, who shall be deemed to have been jointly appointed by the parties. If the candidate chosen by the respective parties is not the same person, the President shall appoint an arbitrator other than those recommended candidates to be the presiding arbitrator.
6. At the request of or with the consent of the parties, the President of the SCIA may recommend a list of more than three (3) candidates for the presiding arbitrator from which each of the parties may remove one or several of the given choices within five (5) days of receipt of the list. The presiding arbitrator shall be determined by the President of the SCIA from the remaining candidates; Where all candidates are excluded, the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA outside the list of the candidates.
Article 31 Sole Arbitrator
Where the arbitral tribunal is composed of a sole arbitrator, the sole arbitrator shall be appointed pursuant to the procedures stipulated in Article 30, Paragraph 2, 4, 5 or 6 of the Rules.
Article 32 Disclosure by Arbitrators
1. Upon being appointed, each arbitrator shall sign a Declaration to undertake to conduct arbitration independently and impartially.
2. The arbitrator shall disclose in the Declaration any circumstances he/she is aware of that are likely to give rise to reasonable doubts as to his/her impartiality or independence.
3. Where any circumstance occurs during the arbitration proceedings after the Declaration is signed which is necessary to be disclosed, the arbitrator shall disclose in writing immediately after such circumstance takes place.
Article 33 Challenge of Arbitrators
1. A party wishing to challenge the arbitrator on the grounds of the information disclosed by the arbitrator shall forward the challenge in writing within ten (10) days from the date of such receipt. Failing to file a challenge within the above time period, the party may not subsequently challenge the arbitrator on the grounds of the information disclosed by the arbitrator.
2. A party which has justifiable doubts as to the impartiality or independence of an arbitrator may challenge that arbitrator in writing and shall state the reasons on which the challenge is based and provide supporting evidence.
3. The challenge by one party shall be promptly communicated to the other party and all the members of the arbitral tribunal.
4. Where an arbitrator is challenged by one party and the other party agrees to the challenge, or the arbitrator being challenged voluntarily withdraws from his/her office, such arbitrator shall no longer be a member of the arbitral tribunal. However, in neither case shall it be implied that the reasons for the challenge are sustained.
5. In circumstances other than those specified in Paragraph 4 of this Article, the President of the SCIA shall make a final decision on the challenge. An arbitrator who has been challenged shall continue to serve on the arbitral tribunal until a final decision on the challenge has been made by the President of the SCIA.
6. A party who, after receiving the notice on the formation of the arbitral tribunal, engages its representative who may give rise to grounds for the challenge of any arbitrator, shall have no right to challenge the arbitrator on those grounds; the right of the other party to challenge the arbitrator shall not, however, be affected. Consequences including but not limited to additional costs due to any resultant delay in the arbitration proceedings under these circumstances shall be borne by the party responsible forgiving rise to the grounds for challenge.
Article 34 Replacement of Arbitrators
1. An arbitrator shall be replaced if he/she becomes unable to fulfil his/her functions due to, inter alia, being challenged or voluntary withdrawal from his/her office or other specific reasons.
2. Where an arbitrator is prevented de jure or de facto from fulfilling his/her functions, or fails to fulfil his/her functions in accordance with the requirements of the Rules, the President of the SCIA shall have the power to replace the arbitrator and the parties and all the members of the arbitral tribunal shall be given opportunity to opine in writing.
3. If the arbitrator to be replaced was appointed by a party, the party shall appoint a substitute arbitrator in the same manner as that of appointing the original arbitrator within five (5) days from the date of the receipt of the notice of replacement; if the party fails to appoint a substitute arbitrator within the prescribed time-limit or if the arbitrator to be replaced was appointed by the President of the SCIA, the substitute arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
4. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, following the replacement of any arbitrator, the arbitral tribunal shall determine whether all or part of the arbitration proceedings having been conducted shall be restarted. If the arbitral tribunal decides to restart all the proceedings, the time-limit for the arbitral award under the Article 50 of the Rules shall be recalculated to start from the date when the arbitral tribunal decides to restart all the proceedings.
Article 35 Continuation of Arbitration by Majority Arbitrators
After the conclusion of the last oral hearing, if an arbitrator of a three- member tribunal is unable to participate in the arbitration proceedings due to certain reasons, the President of the SCIA may replace that arbitrator pursuant to Article 34 of the Rules. Upon the approval of the parties and the President of the SCIA, the other two arbitrators may also continue the arbitration proceedings and render decisions or arbitral awards.
Article 36 Conduct of Hearing Proceedings
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the arbitral tribunal shall have the power to decide procedural matters, and conduct the arbitration in such a manner as it considers appropriate. Under all circumstances, the arbitral tribunal shall act independently and impartially, treat the parties fairly and equitably, and shall afford reasonable opportunities to all parties to make submissions and arguments.
2. Where the arbitral tribunal cannot reach consensus over procedural matters, the arbitration proceedings shall be conducted in accordance with the opinion of a majority of the arbitrators. Where the arbitral tribunal cannot reach a majority opinion, the arbitration proceedings shall be conducted in accordance with the presiding arbitrator’s opinion.
3. The arbitral tribunal may, if it considers it necessary, issue procedural orders or question lists, hold pre-hearing conferences, produce terms of reference, require pre-hearing exchange of evidence or discovery of relevant documents by the parties, request submission of agreed list of issues by the parties, and exercise the power of interpretation to the extent permissible under the governing law.
4. Unless otherwise stipulated by the Rules, the arbitral tribunal shall hold oral hearings. However, the arbitral tribunal may conduct the arbitration only on the basis of documents if the arbitral tribunal deems that oral hearings are unnecessary and the parties so agree.
5. Where the parties agree to conduct the arbitration on the basis of documents only, their agreement shall prevail; except where the arbitral tribunal deems that oral hearings are necessary, in which case it may hold oral hearings.
6. The parties may agree to adopt inquisitorial, adversarial or other approaches in the oral hearings.
Article 37 Notice of Hearing
1. Where an arbitration is to be conducted by way of an oral hearing, the parties shall be notified of the date of the first oral hearing at least ten (10) days prior to the oral hearing. A party having justified reasons may request a postponement of the oral hearing. However, such request must be communicated in writing to the arbitral tribunal at least five (5) days prior to the fixed oral hearing date. The arbitral tribunal shall decide whether or not to postpone the oral hearing.
2. Where a party has justified reasons for failure to submit a request for a postponement of the oral hearing within the time period specified in the preceding Paragraph 1, the arbitral tribunal shall decide whether or not to accept the request.
3. A notice of a subsequent oral hearing and a notice of a postponed oral hearing shall not be subject to the time periods specified in the preceding Paragraph 1.
4. Where the parties have agreed, the arbitral tribunal may hold the hearing earlier than the scheduled time.
Article 38 Place of Hearing
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the place of oral hearings shall be the domicile of the SCIA, or if the arbitral tribunal considers it necessary and with the approval of the SCIA, at another location.
2. Where the parties have agreed to hold an oral hearing at a place other than the domicile of the SCIA, the additional costs so generated shall be borne by the parties. The parties shall deposit in advance for such additional costs in accordance with the proportion agreed by them or decided upon by the SCIA. If such deposit is not made, the hearing shall beheld at the domicile of the SCIA.
Article 39 Default
1. If the Claimant fails to appear at an oral hearing without valid excuses, or withdraws from an on-going oral hearing without the permission of the arbitral tribunal, the Claimant shall be deemed to have withdrawn its Request for Arbitration. In such a case, if the Respondent has filed a counterclaim, the arbitral tribunal shall proceed with the hearing of the counterclaim.
2. If the Respondent fails to appear at an oral hearing without valid excuses, or withdraws from an on-going oral hearing without the permission of the arbitral tribunal, the arbitral tribunal shall make a default hearing, and proceed with the arbitration. In such a case, if the Respondent has filed a counterclaim, the Respondent shall be deemed to have withdrawn its counterclaim.
Article 40 Declaration at the Hearing
At the oral hearing, the arbitral tribunal shall read out a declaration of independence and impartiality; the parties and their representatives, witnesses, appraisers, and other related parties may read out a declaration of good faith and bona fide cooperation.
Article 41 Record of Hearing
1. The arbitral tribunal shall make a written record of the oral hearings, and may make an audio or video record of the oral hearings. The parties may request and obtain a copy of such written record.
2. Arbitrators, parties and/or their representatives, witnesses and/ or other persons involved are required to sign the written record. If the parties or other participants to the arbitration consider that the record has omitted a part of their statements or is incorrect in some respect, they may request for correction thereof. Such request shall be recorded if the arbitral tribunal does not grant the rectification.
3. Upon a joint request by both parties, or a request by one party that has been approved by the arbitral tribunal, or a decision of the arbitral tribunal, the SCIA may appoint one or more stenographers for the arbitral tribunal or use other means to record the oral hearing.
Article 42 Evidence
1. The arbitral tribunal may specify a time period for the parties to produce evidence and the parties shall produce evidence within the specified time period. The arbitral tribunal shall have the power to refuse to admit any evidence produced after that time period.
2. Each party shall bear the burden of proving the facts upon which its claims, defences or counterclaims are based. The arbitral tribunal shall have the power to assign the burden of proof between the parties.
3. If a party bearing the burden of proof fails to produce evidence within the specified time period, or if the produced evidence is not sufficient to support its claims, defences or counterclaims, it shall bear the consequences thereof.
4. Where a party applies to produce witness in the oral hearings, it shall notify in its application to the arbitral tribunal the identity information of the witness, the witness statement and language to be used by the witness.
5. As to the law and other professional issues, the parties may engage an expert witness on such relevant issues to provide written submissions and/or testify in the oral hearings.
6. Where the parties have an agreement specifying the applicable evidence rules, their agreement shall prevail, unless the agreement cannot be implemented or is in conflict with a mandatory provision of the law as it applies to the arbitration proceedings.
Article 43 Examination of Evidence
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the evidence shall be produced at the hearing and may be examined by the parties.
2. Where a case is to be decided on the basis of documents only, or where the evidentiary materials are to be submitted after the hearing, and the parties agree to examine the evidentiary materials in writing,the parties shall submit their written opinions on the documents or the evidentiary materials within the time period specified by the arbitral tribunal.
3. Evidence that the parties have jointly recognised or have no objection to shall be considered as examined evidence.
4. A party who provides forged evidence shall bear the consequences accordingly, and the arbitral tribunal shall have the power to reject the claims or counterclaims submitted by the party so concerned.
Article 44 Investigation by the Arbitral Tribunal
1. Where the arbitral tribunal considers it necessary, or where a party so requests and the arbitral tribunal agrees, the arbitral tribunal may undertake investigations and collect evidence on its own initiative.
2. When investigating and collecting evidence at site, the arbitral tribunal shall notify the parties to be present in a timely fashion when it thinks necessary. In the event that the parties fail to be present after being notified, the investigation and collection of evidence shall proceed without being affected.
3. Information investigated or evidence collected by the arbitral tribunal shall be forwarded to the parties for their comments.
Article 45 Expert Report
1. Where the arbitral tribunal considers it necessary, or where a party so requests and the arbitral tribunal agrees, the arbitral tribunal may appoint experts for, inter alia, appraisal, audit, evaluation, testing or consultancy to produce expert report.
2. The arbitral tribunal may notify the parties to jointly nominate an expert within a time period specified by the arbitral tribunal. If the parties fail to do so, the expert shall be appointed by the arbitral tribunal.
3. The parties shall pay advance deposits for the expert costs in accordance with the proportion agreed by them or decided by the arbitral tribunal. The arbitral tribunal may decide not to conduct the arbitral proceeding provided in Paragraph 1 if the parties do not deposit in advance.
4. Copies of the expert report shall be forwarded to the parties for their comments. The arbitral tribunal may notify the expert to participate at an oral hearing to explain the expert report if the arbitral tribunal considers it necessary, or if a party so requests.
Article 46 Suspension of the Arbitration Proceedings
1. Where parties request a suspension of the arbitration proceedings, or under circumstances where such suspension is necessary pursuant to relevant law or provisions of the Rules, the arbitration proceedings may be suspended by the arbitral tribunal. Where the arbitral tribunal has not yet been formed, such decision shall be made by the SCIA.
2. The arbitration proceedings shall resume as soon as the reason for the suspension no longer exists.
Article 47 Withdrawal and Dismissal
1. A party may withdraw its claims or counterclaims in its entirety. In the event that the Claimant withdraws its claims in its entirety, the arbitral tribunal shall proceed with its examination of the counterclaims and render an arbitral award thereon. In the event that the Respondent withdraws its counterclaims in its entirety, the arbitral tribunalshall proceed with the examination of the claims and render an arbitral award thereon.
2. A case shall be dismissed by the arbitral tribunal if the claims and counterclaims have been withdrawn in their entirety. Where a case is to be dismissed prior to the formation of the arbitral tribunal, the SCIA shall make a decision on the dismissal. The SCIA or the arbitral tribunal shall have the power to determine that the relevant arbitration fees and costs be borne by the party that withdraws the claims or counterclaims, unless otherwise agreed by the parties where the agreement of the parties shall prevail.
3. Where a party requests to withdraw its claims or counterclaims in its entirety after the oral hearings, the arbitral tribunal may give the other party a reasonable opportunity to express its opinions. Should the other party make a reasonable objection, and the arbitral tribunal considers that there is a justified reason to resolve the dispute through rendering the arbitral award, the arbitral tribunal shall have the power to continue the arbitration proceedings.
Article 48 Mediation by the Arbitral Tribunal
1. Where the parties wish to mediate, the arbitral tribunal may conduct mediation during the arbitration proceedings. If the parties agree that the arbitrator(s) conduct the mediation, the arbitrator(s) who have conducted the mediation can continue to serve on the arbitral tribunal in the subsequent arbitration proceedings, unless otherwise agreed by the parties or provided by the applicable laws.
2. The arbitral tribunal may mediate in a manner it considers appropriate. With the consent of each party, the mediation may be conducted by all or some members of the arbitral tribunal.
3. Where either party requests for the joinder of an additional party in the mediation proceedings and the other parties and the said additional party so agree, the arbitral tribunal may notify the said additional party to join the mediation.
4. During the mediation, the arbitral tribunal shall terminate the mediation if either party so requests or if the arbitral tribunal deems that further mediation would be futile.
5. Where mediation reaches a settlement, the parties may withdraw their claims or counterclaims, or may request the arbitral tribunal to render an arbitral award or a mediation statement in accordance with the terms of the settlement agreement.
6. Where mediation fails, acceptance or opposition, expressed in any statement, view, opinion, proposal or proposition, by either party or by the arbitral tribunal in mediation, cannot be invoked by either party as grounds for supporting any claims, defences or counterclaims in the subsequent arbitration proceedings, judicial proceedings, or any other proceedings.
Article 49 Settlement, Mediation and Negotiation Facilitation
1. The parties may reach a settlement agreement by themselves, or apply to the SCIA Mediation Center, or other mediation institutions recognised by the SCIA for mediation, or may apply for negotiation to the SCIA Negotiation Facilitation Center.
2. Where a settlement agreement is reached in accordance with Paragraph 1, the parties may apply to the arbitral tribunal for rendering an arbitral award or a mediation statement in accordance with the terms of the settlement agreement or apply to withdraw the arbitration case. In the event the parties have not requested for arbitration or the arbitral tribunal has not yet been formed, and the parties apply for rendering an arbitral award or a mediation statement in accordance with the settlement agreement, unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the President of the SCIA shall appoint a sole arbitrator to form the arbitral tribunal to conduct the arbitration inappropriate procedures and render an arbitral award or a mediation statement in due course. The specific procedures and time-limitshall not be subject to other provisions of the Rules.
3. The SCIA or the arbitral tribunal shall have the power to request the parties to make statements to ensure the legitimacy and authenticity of the settlement agreement, and to promise not to harm the interest of third persons to the case or the public interest, and other relevant circumstances. If the arbitral tribunal has reasonable doubts on the legitimacy and authenticity of the settlement agreement, or believes that rendering an arbitral award or a mediation statement in accordance with such settlement agreement may be prejudicial to the interest of third persons to the case or the public interest, it shall reject the application to render an arbitral award or a mediation statement in accordance with the terms of the settlement agreement.
Article 50 Time-limit for the Award
1. For cases under Article 2, Paragraph 1(a) and (b), the arbitral tribunal shall render an arbitral award within six (6) months from the date on which the arbitral tribunal is formed.
2. For cases under Article 2, Paragraph 1(c), the arbitral tribunal shall render an arbitral award within four (4) months from the date on which the arbitral tribunal is formed.
3. For cases under Article 2, Paragraph 1 that may apply the Expedited Procedure under Chapter IX, the arbitral tribunal shall render an arbitral award within two (2) months from the date on which the arbitral tribunal is formed.
4. Where there are special circumstances or adequate reasons justifying an extension of the duration of the arbitration, the SCIA may approve an appropriate extension upon the request of the arbitral tribunal.
5. The following periods shall be excluded when calculating the time-limit in the preceding paragraphs:
(a) Period of appointing experts for, inter alia, appraisal, audit, evaluation, testing, consultancy pursuant to Article 45;
(b) Any period of settlement, mediation and negotiation facilitation pursuant to Article 48 and Article 49; and
(c) Any suspension period pursuant to relevant provisions of law and the Rules.
Article 51 Rendering of Arbitral Award
1. The arbitral tribunal shall independently and impartially render an arbitral award in a fair and reasonable manner, based on the facts and in accordance with the applicable laws and the universally acknowledged legal principles, and with reference to commercial practices.
2. Where the parties have agreed on the law as it applies to the merits of their dispute, the parties’ agreement shall prevail. In the absence of such an agreement or where such agreement is in conflict with a mandatory provision of the law of the place of arbitration, the arbitral tribunal shall determine which law is applicable.
3. The arbitral tribunal shall state in the arbitral award the claims, the facts of the dispute, the reasons on which the arbitral award is based, the decision on the claims, the allocation of the arbitration costs, the date of the arbitral award, and the place of the arbitration. The facts of the dispute and the reasons on which the arbitral award is based may not be stated in the arbitral award if the parties have so agreed, or if the arbitral award is rendered in accordance with the terms of a settlement agreement between the parties. The arbitral tribunal has the power to determine the specific time period for the parties to carry out the arbitral award and the liabilities for failure to do so within the specified time period.
4. Where a case is arbitrated by an arbitral tribunal formed of three arbitrators, the arbitral award shall be rendered by all three arbitrators or a majority of the arbitrators. A written dissenting opinion shall be kept with the file and may be notified to the parties together with the arbitral award. Such dissenting opinion shall not form a part of the arbitral award. Where the arbitral tribunal cannot reach a majority opinion, the arbitral award shall be rendered in accordance with the presiding arbitrator’s opinion. The written opinions of the other arbitrators shall be kept with the file and may be notified to the parties together with the award. Such written opinions shall not form a part of the award.
5. The arbitral award shall be signed by arbitrators. An arbitrator who has a dissenting opinion may or may not sign his/her name on the arbitral award.
6. The date on which the arbitral award is rendered shall be the date on which the arbitral award comes into legal effect.
7. The seal of the SCIA shall be affixed to the arbitral award.
8. The arbitral award is final and binding upon the parties, except for cases in which the parties agree to apply the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure. The effectiveness of such arbitral award shall be determined according to article 68 of the Rules and the“Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure of the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration”.
Article 52 Partial Award
Where the arbitral tribunal considers it necessary, or where a party so requests and the arbitral tribunal agrees, the arbitral tribunal may render a partial award on any part of the claim before rendering the arbitral award in accordance with Article 51. A partial award is final and binding upon the parties.
Article 53 Scrutiny of the Draft Award
The arbitral tribunal shall submit its draft award to the SCIA for scrutiny before signing. The SCIA may suggest modifications on the form of the draft award and may also draw the attention of the arbitral tribunal to substantive issues without affecting its independence.
Article 54 Correction of the Award and Additional Award
1. Within thirty (30) days after its receipt of the arbitral award, either party may request the arbitral tribunal in writing for a correction of any clerical, typographical or computational errors, or any errors of a similar nature contained in the award. If such an error does exist in the arbitral award, the arbitral tribunal shall make a correction in writing within thirty (30) days of receipt of the written request for the correction.
2. Either party may, within thirty (30) days from its receipt of the arbitral award, request the arbitral tribunal in writing for an additional award on any claim which was advanced in the arbitration proceedings but was omitted from the arbitral award. If such an omission does exist, the arbitral tribunal shall render an additional award within thirty (30) days of receipt of the written request.
3. The arbitral tribunal may, on its own initiative, make corrections of the arbitral award or render additional award in writing, within a reasonable time period after the arbitral award is rendered.
4. Such correction of award or additional award in writing shall form a part of the arbitral award.
Article 55 Re-arbitration
1. Where a competent court notifies the case be re-arbitrated in accordance with provisions of law, the case shall be arbitrated by the original arbitral tribunal. Where the member(s) of the original arbitral tribunal is/are unable to fulfil his/her duties due to being challenged or voluntary withdrawal from his/her office or other specific reasons, a substitute arbitrator shall be appointed under Article 34.
2. The arbitral tribunal shall decide on the specific procedures for the case to be re-arbitrated.
3. The arbitral tribunal shall render an arbitral award after the re- arbitration in accordance with the Rules.
4. The re-arbitral award shall replace the original award. The parties shall carry out the re-arbitral award.
Article 56 Application
1. Expedited Procedure shall apply to any case where the amount in dispute does not exceed RMB10,000,000 Yuan; or to any case where the amount in dispute exceeds RMB10,000,000 Yuan but the parties agree in writing that the Expedited Procedure shall apply; or to any case where the parties agree to apply the Expedited Procedure or Summary Procedure.
2. Where the amount in dispute is not clear, the SCIA shall determine whether or not to apply the Expedited Procedure after a full consideration of relevant factors, including but not limited to the complexity of the case and the interests involved.
Article 57 Defence and Counterclaim
1. The Respondent shall submit its Statement of Defence and evidentiary materials within ten (10) days after receipt of the Notice of Arbitration.
2. The Respondent shall submit its counterclaim (if any) in writing within ten (10) days after receipt of the Notice of Arbitration. The Claimant shall submit its Statement of Defence to the Respondent’s counterclaim within ten (10) days after receipt of the Notice of Acceptance of Counterclaim.
Article 58 Formation of Arbitral Tribunal
For any case that applies the Expedited Procedure, an arbitral tribunal of a sole arbitrator shall be formed in accordance with Article 31 to hear the case.
Article 59 Conduct of Hearing Proceedings
The arbitral tribunal may conduct the arbitration in the manner it considers appropriate. The arbitral tribunal may decide whether to conduct the arbitration solely on the basis of the written materials and evidence submitted by the parties or to hold an oral hearing.
Article 60 Notice of Hearings
1. For an arbitration conducted by way of an oral hearing, after the arbitral tribunal has fixed a date for oral hearing, the parties shall be notified at least seven (7) days prior to the oral hearing. A party having justified reasons may request a postponement of the oral hearing. However, such request shall be communicated in writing to the arbitral tribunal at least three (3) days prior to the fixed oral hearing date. The arbitral tribunal shall decide whether or not to postpone the oral hearing.
2. Where a party has justified reasons for failure to submit a request for a postponement of the oral hearing within the time period specified in the preceding Paragraph 1, the arbitral tribunal shall decide whether or not to accept the request.
3. A notice of a subsequent oral hearing, as well as a notice of a postponed oral hearing, shall not be subject to the time-limit specified in the preceding Paragraph 1.
Article 61 Change of Procedure
1. The application of Expedited Procedure shall not be affected by any amendment to the claim or by the filing of a counterclaim.
2. Where the amount in dispute of the amended claim or that of the counterclaim exceeds RMB 10,000,000 Yuan, upon one of the parties’ request or the suggestion of the arbitral tribunal, and if the SCIA considers it necessary, the Expedited Procedure may be changed to the general procedure by the SCIA.
3. For any case that originally applies the general procedure, if the Claimant amends its claims before the formation of the arbitral tribunal and the amount in dispute as amended does not exceed RMB 10,000,000 Yuan, the Expedited Procedure shall apply. The application of the general procedure shall not be affected by any amendment to the claim or by the filing of a counterclaim after the formation of the arbitral tribunal.
Article 62 Other Provisions
The relevant provisions in the other Chapters of the Rules shall apply to matters not covered in this Chapter.
Article 63 Arbitration Fees and Costs
1. The parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in advance to the SCIA in accordance with the “Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration” stipulated by the SCIA.
2. Where the parties agree to apply other arbitration rules, the SCIA may charge in accordance with the schedule of fees and costs of arbitration stipulated by such other arbitration rules. If such other arbitration rules lack such a schedule, the Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration adopted by the SCIA shall apply.
3. During the course of the arbitration proceedings, where the parties fail to pay in advance the relevant fees and costs as required, the SCIA shall so inform the parties in order that one or another of them may make the required payment. If such payment is not made, the SCIA may order the suspension of the arbitration proceedings, or regard such as the total withdrawal of the claims or counter-claims of the parties.
4. The Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration which is attached hereto forms an integral part of the Rules.
Article 64 Allocation of Fees
1. The arbitral tribunal has the power to determine in the arbitral award the arbitration fees and other expenses to be borne by the parties. Such fees and other expenses include fees and actual expenses payable under the Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration, and the reasonable legal fees and other expenses incurred by the parties for conducting the arbitration.
2. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties or stipulated in the Rules, the arbitration fees and costs shall in principle be borne by the losing party. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the arbitral tribunal may decide to assign the arbitration fees and costs among the parties according to the proportions it deems appropriate for the circumstances. If the parties reach a settlement either on their own initiative or as a result of mediation by the arbitral tribunal, the parties may reach an agreement upon the payment of such fees and costs.
3. In case of any breach of the Rules or failure to carry out the arbitral tribunal’s decisions by any party which causes delay in the arbitration proceedings, the allocation of arbitration fees and costs to such party shall not be subject to the provisions under the preceding paragraph. Where other costs are incurred or increased due to delay in the arbitration proceedings, such party shall also bear the costs so incurred or increased.
4. The arbitral tribunal shall, at the request of a party, have the power to determine in the arbitral award that the losing party bears the reasonable costs and expenses of the successful party incurred in relation to the arbitration proceedings, including but not limited to the attorney’s fees, the costs of preservation measures, travel and accommodation expenses, notarial fees and witness expenses. While determining the amount of these costs and expenses, the arbitral tribunal shall take into account the outcome and complexity of the case, the actual workload of the parties or their representatives, the amount in dispute and any other relevant factors.
Article 65 Calculation of Time-limits
1. Periods of time specified in or fixed under the Rules shall start to run on the day following the date a notification or communication is deemed to have been made.
2. When the day next following such date is a public holiday, or a non-business day in the country where the notification or communication is deemed to have been made, the period of time shall commence on the first following business day. Public holidays and non-business days within the period concerned are included in the calculation of the period of time. If the last day of the relevant period of time is a public holiday or a non-business day, the period of time shall expire at the end of the first following business day.
3. If a party breaches a time-limit because of force majeure events or other justifiable reasons, it shall inform the SCIA within a reasonable time period and may apply for an extension of time within ten(10) days after such reasons no longer exist. The arbitral tribunal shall decide on the request. Where the arbitral tribunal has not yet been formed, such decision shall be made by the SCIA.
Article 66 Confidentiality
1. Arbitration shall not be open to the public.
2. Where all the parties agree that an oral hearing be open to the public, the arbitral tribunal shall decide whether the oral hearing shall be open to the public.
3. Where an oral hearing is not to be open to the public, the parties and their representatives, witnesses, interpreters, arbitrators, experts consulted or appraisers appointed by the arbitral tribunal, persons recording the oral hearings, staff of the SCIA and other relevant persons shall keep any substantive or procedural matters relating to the case confidential, unless otherwise stipulated under the laws.
Article 67 Application of Information Technology
Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal may decide to conduct all or part of the arbitral proceedings by virtue of information technology, including but not limited to online registration, service, oral hearing, and examination of evidence.
Article 68 Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure
1. Unless prohibited by the laws of the place of arbitration, where the parties have agreed on submitting to the SCIA for appellate arbitration in respect of the award rendered by the arbitral tribunal according to Chapter VIII herein, their agreement shall prevail. The optional appellate arbitration procedure shall not apply to the expedited procedure of the Rules.
2. The optional appellate arbitration procedure shall be conducted in accordance with the “SCIA Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure”.
Article 69 Waiver of Objection
A party shall be deemed to have waived its right to object where it knows or should have known that any provision of the Rules, other arbitration rules applicable to the arbitration proceedings, decisions of the arbitral tribunal or any term under the arbitration agreement has not been complied with and yet participates in or proceeds with the arbitration proceedings without promptly submitting its objection in writing to such non-compliance.
Article 70 Limitation of Liability
The arbitrator(s), the SCIA and its related persons shall not be liable to any person for any act or omission related to the arbitration, except for intentional misconduct.
Article 71 Interpretation of the Rules
1. The headings of the articles in the Rules shall not be construed as interpretations of the contents of the provisions contained therein.
2. The Rules shall be interpreted by the SCIA.
3. Unless otherwise stated, other documents issued by the SCIA shall not constitute integral parts of the Rules.
Article 72 Coming into Force
The Rules shall be effective as from 21 February 2019 upon the deliberation and approval of the Council of the SCIA. As of the date of the Rules’ coming into force, all cases accepted by the SCIA shall be governed by the Rules. For cases accepted by the SCIA before the Rules come into force, the Rules effective at the time of acceptance shall apply, or where the parties agree, the Rules shall apply.
I. Prepaid Arbitration Fees and Costs
Schedule I
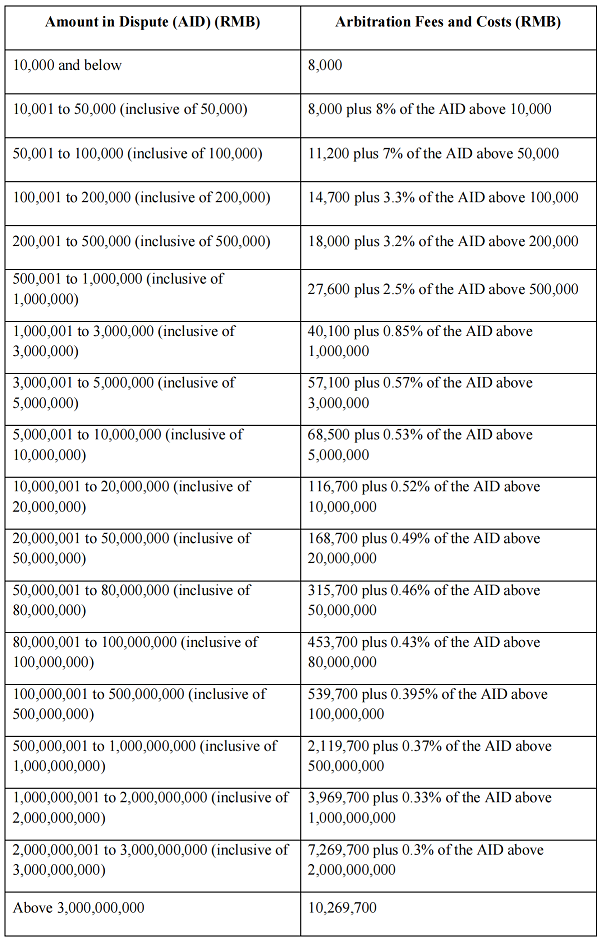
1. Unless otherwise provided by the SCIA, This Schedule I applies to arbitration cases under Article 2 (1) of the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
2. The parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in advance in accordance with the rates under this Schedule I for their respective claim or counterclaim.
3. The AID shall be on the basis of the amount of money claimed by the parties. The actual amount in dispute shall prevail if it is inconsistent with the claimed amount in dispute. Where no monetary claim is specified or the amount in dispute is not clear, the amount of arbitration fee shall be determined by the SCIA in consideration of the specific rights and interests involved in the disputes.
4. If the arbitration fee is charged in a foreign currency, an amount of the foreign currency equivalent to the corresponding RMB value specified in Schedule I shall be paid.
5. The SCIA may charge for other disbursements reasonably incurred in accordance with the relevant provisions under the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
6. Unless otherwise provided in the SCIA Arbitration Rules, the remuneration of the arbitrator(s) shall be paid from the arbitration fees and costs collected by the SCIA. The SCIA shall take into account of factors such as the time spent by the arbitrator(s) to handle the case, the complexity of the case, and the diligence and efficiency of the arbitrator(s) while determining the remuneration of the arbitrator(s).
II. Advance Payment of Arbitration Fees and Costs in Installments
In cases whereby a large amount of arbitration fees and costs is payable under Article 1 of this Schedule I or there are other special circumstances in any arbitration case, the SCIA may, upon the request of the parties, agree to allow the parties to make the advance payment of the arbitration fees and costs in installments, provided that:
1. No less than one-third of the total arbitration fees and costs is paid upon request for arbitration;
2. No less than half of the total arbitration fees and costs is paid by the time the arbitral tribunal is formed; and
3. The total arbitration fees and costs shall be paid in full by the time of the hearing.
III. Arbitration Fees and Costs in Cases Where an Arbitral Award or Mediation Statement is Made in Accordance with the Settlement Agreement
In accordance with Article 48 (5), Article 49 (1) and (2) of the SCIA Arbitration Rules, if the parties request an Arbitral Award or a Mediation Statement in accordance with the content of the Settlement Agreement, the fees and costs shall be charged as follows:
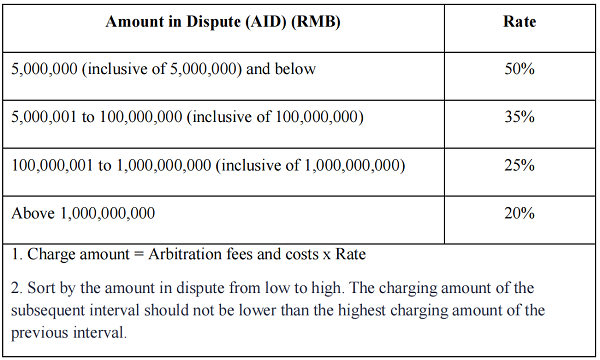
1.If a settlement is reached before applying for arbitration, the parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in accordance with Schedule II.
Schedule II
2. If a settlement is reached after the acceptance of the arbitration application and before the formation of the arbitral tribunal, 50% of the arbitration fees and costs will be returned.
3. If a settlement is reached before the first hearing after the formation of the arbitral tribunal, 40% of the arbitration fees and costs will be returned.
4. If a settlement is reached after the hearing, 20% of the arbitration fees and costs will be returned.
5. For cases decided on the basis of documents only, if a settlement is reached after the formation of the arbitral tribunal, 20%-40% of the arbitration fees and costs will be returned considering factors such as the progress and complexity of the case and the workload of the arbitral tribunal.
6. If the amount in dispute involved in the settlement reached by the parties after the commencement of the arbitration proceedings exceeds the original arbitration claim, the arbitration fees and costs shall be calculated on the basis of the increased actual amount of the dispute.
7. If the parties apply for mediation or negotiation facilitation to the SCIA Mediation Center or Negotiation Facilitation Center in advance yet fail to reach a settlement and apply for arbitration, the prepaid arbitration fees and costs shall deduct the mediation or negotiation facilitation fees already paid by the parties.
IV. Arbitration Fees and Costs for Dismissed Cases
Unless otherwise provided by the SCIA, the fees and costs for dismissed cases under Article 47 (2) of the SCIA Arbitration Rules shall be as follows:
1. If the case is dismissed prior to the formation of arbitral tribunal, 80% of the arbitration fees and costs shall be returned.
2. If the case is dismissed after the formation of the arbitral tribunal and before the first hearing, 60% of the arbitration fees and costs shall be returned.
3. If the case is dismissed after the first hearing, 40% of the arbitration fees and costs shall be returned.
4. For cases decided on the basis of documents only, if the dismissal is made after the formation of the arbitral tribunal, 40%-60% of the arbitration fees and costs shall be returned considering the progress, complexity of the case, and the workload of the arbitral tribunal.
V. Arbitration Fees and Costs for Consolidated Arbitration
For consolidated arbitration conducted in accordance with Article 18 of the SCIA Arbitration Rules, 20% of the arbitration fees and costs shall be returned for each case.
VI. Arbitration Fees and Costs in Relation to Arbitral Cases Governed by UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules
As for the international and foreign-related arbitration cases and those related to the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, the Macao Special Administrative Region and Taiwan Region governed by the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules under Article 3 (4) , and for arbitral cases related to the investment disputes under Article 2 (2), the arbitration fees and costs shall be charged by the SCIA in accordance with the SCIA Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (“Guidelines”) as follows:
1. Registration Fee
The Registration fee shall be RMB 5,000, which is non-refundable under any circumstances.
2. Administrative Fee
The administrative fee shall include the costs and expenses incurred from providing the service under Article 4 (1) of the Guidelines in relation to the following:
(1) Appointment of Arbitrators (RMB)
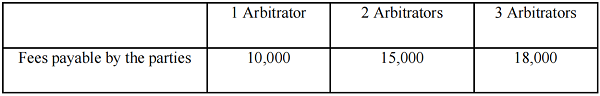
(2) Decision on the Challenge of Arbitrator
An amount of RMB 20,000 shall be charged for each decision on the challenge of arbitrator(s).
(3) Financial Management of Arbitration case
The SCIA shall charge a financial management fee, being 0.1% of the total amount of fees in custody of SCIA. The minimum management fee chargeable shall be RMB 1,000 and shall be capped at a maximum of RMB 100,000.
(4) Services under Article 4 (2) of the Guidelines
The SCIA shall charge disbursements incurred from services provided by SCIA under Article 4 (2) of the Guidelines or from other administrative services requested by the parties or the arbitral tribunal, which shall be charged on actual basis.
VII. Arbitration Fees and Costs in Relation to Application of other Arbitration Rules
Schedule III
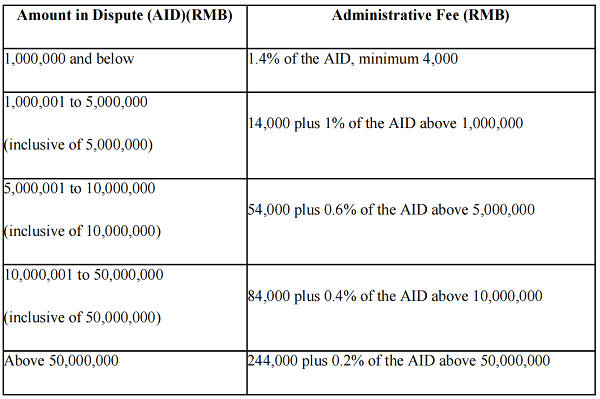
1. This Schedule III shall apply if the parties agree to submit to the SCIA for arbitration in accordance with the arbitration rules other than the SCIA Rules and the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules, and that the SCIA shall provide the administrative services for the arbitration proceedings.
2. A registration fee of RMB 10,000 shall be payable upon application for arbitration, for the purposes of examining the application for arbitration, initiating the arbitration proceedings, computerizing management, filing management and correspondence. The registration fee is non-refundable.
3. The parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in advance in accordance with the rates under this Schedule III for their respective claim or counterclaim. The AID referred to in this Schedule III shall be on the basis of the sum amount of money claimed by the parties. The actual amount in dispute shall prevail if it is inconsistent with the claimed amount in dispute. Where no monetary claim is specified or the amount in dispute is not clear, the amount of administrative fee shall be determined by the SCIA in consideration of the specific rights and interests involved in the disputes.
4. If the arbitration fee is charged in a foreign currency, the foreign currency shall be payable at an amount equivalent to the corresponding amount in RMB under this Schedule III.
5. The SCIA can charge for other disbursements reasonably incurred in accordance with the relevant provisions under the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
6. The administrative fee payable to the SCIA shall not include the remuneration of the arbitrator(s).
VIII. Remuneration of the Arbitrators Determined by Agreement between the Parties and the Arbitrators and the Payment Thereof
1. The remuneration of the arbitrators may be determined by agreement. Any agreement- based method of determination shall require the unanimous consent of all parties and shall be applicable to all members of the arbitral tribunal
2. The fees and expenses of arbitrators determined in accordance with the fee arrangements shall be reasonable in amount, taking into account the amount in dispute, the complexity of the subject- matter, the time spent by the arbitrators and any other relevant circumstances of the case. According to the above circumstances, the SCIA shall have the power to make any necessary adjustment to the fees and expenses of arbitrators, which will be binding upon the arbitral tribunal.
3. Where the parties agree that the remuneration of the arbitrator shall be calculated on an hourly basis:
(1) The hourly rate of an arbitrator designated by one party shall be agreed upon between that party and the designated arbitrator; the hourly rate for sole arbitrator and presiding arbitrator shall be agreed upon between the arbitrator and all parties; if the parties and the arbitrator fail to agree on the hourly rate within the agreed period or as notified by the SCIA, the hourly rate of the arbitrator shall be determined by the SCIA.
(2) In principle, the hourly rate of arbitrator shall not exceed RMB 6,000, unless agreed by the parties.
(3) At different stages of the arbitration proceedings, the parties shall pay in advance an appropriate amount of security for the arbitrators' remuneration in accordance with the notice of the SCIA. If the amount paid by the parties exceeds the actual remuneration due to the arbitrators, the SCIA shall refund the excess amount to the parties after the arbitral tribunal issues the final award.
4. The SCIA is entitled to adjust the arbitration fees and costs payable by the parties in advance based on the circumstances of the case concerned.
5. If the parties have objections to the determination of the arbitrator's remuneration by agreement or to the amount thereof, it shall be determined by the SCIA.
6. In cases where the remuneration of the arbitrators is established by agreement, the payment of such remuneration shall be decided by the arbitral tribunal in accordance with applicable arbitration rules and the relevant provisions of this Schedule.
IX. Arbitration Fees and Costs in relation to Appointment of Emergency Arbitrators
Schedule IV
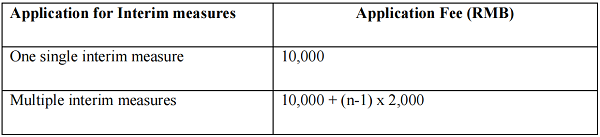
(where “n” refers to the number of interim measures applied for by the parties)
This Schedule IV shall apply if a party applies to the SCIA for appointment of an emergency arbitrator for the interim measure(s) under Article 26 of the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
SCIA Arbitration Rules for Financial Loan Disputes
(Adopted by the Second Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, effective as from February 21, 2019. Amended for the first time by the Second Council of SCIA at its fourteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from October 1, 2020. Amended for the second time by the Second Council of SCIA at its eighteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from February 21, 2022. Amended for the third time by the Third Council of SCIA at its thirteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from July 1, 2025.)
MODEL ARBITRATION CLAUSE
Any dispute arising from or in connection with this contract shall be submitted to the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (the SCIA) for arbitration in accordance with the SCIA Arbitration Rules for Financial Loan Disputes.
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Rules for Financial Loan Disputes
CONTENTS
Article 1 Purpose
Article 2 Scope of Application
Article 3 Arbitration Fees and Costs
Article 4 Time Limit for Defence and Counterclaim
Article 5 Formation of the Arbitral Tribunal
Article 6 Conduct of Hearing Proceedings
Article 7 Notice of Hearings
Article 8 Time-limit for the Arbitral Award
Article 9 Change of Procedure
Article 10 Other Matters
Article 11 Interpretation of the Rules
Article 12 Coming into Force
Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs for Financial Loan Disputes
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Rules for Financial Loan Disputes
Article 1 Purpose
The Rules are formulated by the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (also known as the South China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission, the Greater Bay Area International Arbitration Center, or the Shenzhen Arbitration Commission, formerly known as the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission South China Sub-commission or the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission Shenzhen Sub - commission; hereinafter as the “SCIA”) in accordance with the Arbitration Law of the People’s Republic of China and the SCIA Arbitration Rules for the purpose of efficient and speedy resolution of financial loan disputes.
Article 2 Scope of Application
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the Rules shall apply to arbitration cases accepted by the SCIA which involve disputes over bank loans and their security contracts governed by the laws of the People's Republic of China.
2. For arbitration cases involving the following contractual disputes accepted by the SCIA to which the parties agree to apply the Rules, the SCIA shall decide whether to apply the Rules based on their merits:
(a) Inter-bank lending disputes;
(b) Inter-company lending disputes;
(c) Private lending disputes;
(d) Small loan contract disputes;
(e) Non-performing financial loan transfer contract disputes;
(f) Non-performing financial loan recovery disputes; or
(g) Other contract disputes.
Article 3 Arbitration Fees and Costs
1. The parties shall pay the applicable arbitration fees and costs to the SCIA in accordance with the Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs for Financial Loan Disputes prescribed by the SCIA.
2. The Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs for Financial Loan Disputes which is attached hereto forms an integral part of the Rules.
Article 4 Time Limit for Defence and Counterclaim
1. The Respondent shall submit its Statement of Defence and evidentiary materials within seven (7) days after receipt of the Notice of Arbitration.
2. The Respondent shall submit its counterclaim (if any) in writing within seven (7) days after receipt of the Notice of Arbitration. The Claimant shall submit its Statement of Defence to the Respondent’s counterclaim within seven (7) days after receipt of the Notice of Acceptance of Counterclaim.
Article 5 Formation of the Arbitral Tribunal
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties or decided by the SCIA, an arbitral tribunal shall be composed of a sole arbitrator.
2. Within seven (7) days after receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, the parties shall jointly appoint, or jointly entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, the sole arbitrator, failing which, the sole arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
3. Where the arbitral tribunal is composed of 3 arbitrators, each of the parties shall appoint, or entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, one arbitrator and jointly appoint, or jointly entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, the presiding arbitrator, within seven (7) days after receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, failing which, the arbitrators shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
Article 6 Conduct of Hearing Proceedings
The arbitral tribunal may conduct the arbitration in the manner it considers appropriate. The arbitral tribunal may decide whether to conduct the arbitration solely on the basis of the written materials and evidence submitted by the parties or to hold an oral hearing.
Article 7 Notice of Hearings
After the arbitral tribunal has fixed a date for the first oral hearing, the parties shall be notified at least five (5) days prior to the oral hearing.
Article 8 Time-limit for the Arbitral Award
The arbitral tribunal shall render an arbitral award within one (1) month from the date on which the arbitral tribunal is formed. Where there are special circumstances or adequate reasons justifying an extension of the duration of the arbitration, the SCIA may approve an appropriate extension upon the request of the arbitral tribunal.
Article 9 Change of Procedure
For cases to which the Rules are applicable, upon the request of the parties or the suggestion of the arbitral tribunal and by taking into consideration such factors as the amount in dispute and the complexity of the cases, the SCIA may decide to apply any other arbitration procedure provided in the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
Article 10 Other Matters
The SCIA Arbitration Rules shall apply to matters not covered herein.
Article 11 Interpretation of the Rules
1. The headings of the articles in the Rules shall not be construed as interpretations of the contents of the provisions contained therein.
2. The Rules shall be interpreted by the SCIA.
Article 12 Coming into Force
The Rules shall be effective as from 21 February 2019.
Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs for Financial Loan Disputes
Schedule
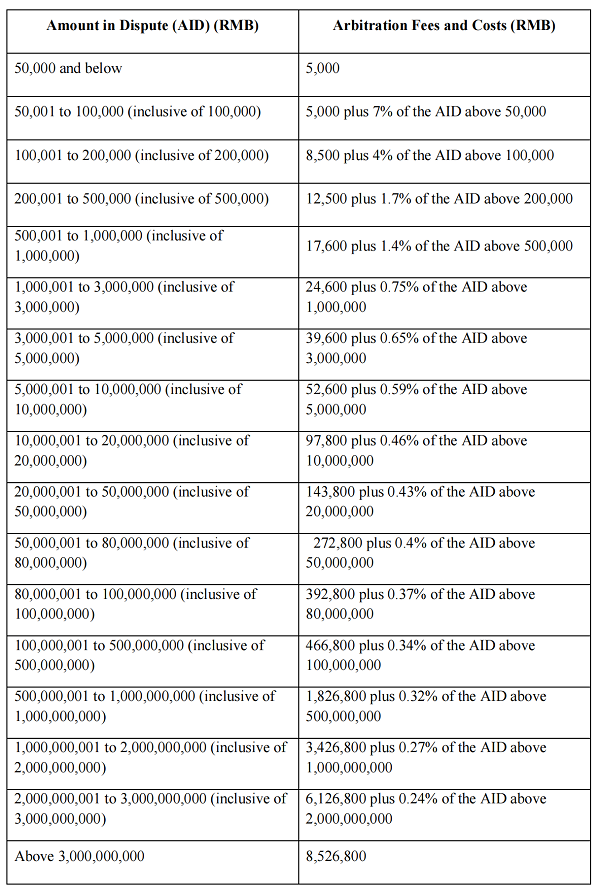
1. The parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in advance in accordance with the rates under this Schedule for their respective claim or counterclaim.
2. The AID shall be on the basis of the amount of money claimed by the parties. The actual amount in dispute shall prevail if it is inconsistent with the claimed amount in dispute. Where no monetary claim is specified or the amount in dispute is not clear, the amount of arbitration fees and costs shall be determined by the SCIA in consideration of the specific rights and interests involved in the disputes.
3. If the arbitration fee is charged in a foreign currency, an amount of the foreign currency equivalent to the corresponding RMB value specified in this schedule shall be paid.
4. In addition to the arbitration fees and costs set forth in this Schedule, the SCIA may charge for other disbursements reasonably incurred.
SCIA Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure
(Adopted by the Second Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, effective as from February 21, 2019. Amended by the Second Council of SCIA at its eighteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from February 21, 2022.)
Parties who want to resolve their dispute in accordance with Article 68 of the SCIA Arbitration Rules and the SCIA Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure may include the following model clause to a contract:
Any dispute arising from or in connection with this contract shall be submitted to the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (the SCIA) for arbitration. The parties grant each other the right to appeal to the SCIA against the award or awards rendered by the arbitral tribunal. The appellate tribunal renders the final award. The place of arbitration shall be. (State the country or jurisdiction where the Appellate Arbitration is not prohibited)
Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure of the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration
CONTENTS
Article 1 Basis
Article 2 Scope of Application
Article 3 Commencement of the Appellate Arbitration Procedure
Article 4 Application for Appellate Arbitration
Article 5 Composition of the Appellate Arbitral Tribunal
Article 6 Effectiveness of the Original Award
Article 7 Appellate Award
Article 8 Allocation of Fees and Costs
Article 9 Miscellaneous
Article 10 Interpretation and Implementation
Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure of the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration
Article 1 Basis
The Guidelines for the Optional Appellate Arbitration Procedure of the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (hereinafter, the “Guidelines”) are formulated by the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (also known as the South China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission, Greater Bay Area International Arbitration Center, or Shenzhen Arbitration Commission, hereinafter the “SCIA”) in accordance with the Arbitration Rules of Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (hereinafter the “Arbitration Rules”).
Article 2 Scope of Application
Unless prohibited by the laws of the place of arbitration, the Guidelines shall apply where the parties agree that the award rendered by the arbitral tribunal according to Chapter VIII of the Arbitration Rules (hereinafter, the “Original Award”) may be submitted to the SCIA for appellate arbitration in accordance with Article 68 of the Arbitration Rules.
Article 3 Commencement of the Appellate Arbitration Procedure
1. The appellant shall apply for appellate arbitration within fifteen
(15) days of its receipt of the Original Award.
2. The appellant shall submit the Application for Appellate Arbitration in accordance with Article 4 of the Guidelines, attach the supporting evidentiary materials, and pay the appellate arbitration fees and costs in advance within the required time-limit in accordance with the notice from the SCIA. The provisions of the Arbitration Rules shall apply mutatis mutandis to the fees and costs of the appellate arbitration.
Article 4 Application for Appellate Arbitration
The Application for Appellate Arbitration shall include:
1. the arbitration agreement on appellate arbitration between the appellant(s) and the appellee(s);
2. the element(s) of the Original Award that are being appealed;
3. the application for appeal; and
4. the facts and grounds on which the request for appeal is based.
Article 5 Composition of the Appellate Arbitral Tribunal
1. The appellate arbitral tribunal shall be composed of three (3) arbitrators, with one (1) serving as the presiding arbitrator. No member of the appellate arbitral tribunal shall be selected from the original arbitral tribunal and all shall be selected by the President of the SCIA from the Panel of Arbitrators of Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration.
2. Where two or more parties have filed for appeal with respect to the same Original Award, the case shall be arbitrated by the same appellate arbitral tribunal.
Article 6 Effectiveness of the Original Award
1. Where an appeal may be filed in accordance with the Guidelines, the Original Award shall not be deemed final and effective before the expiration of the period for filing for appeal.
2. If no party files for appeal or applies to withdraw its filing within the time-limit specified in Article 3 of the Guidelines, the Original Award shall be deemed final and effective as of the date of expiration of such time-limit.
3. If the appellant applies to withdraw its filing after the time-limit specified in Article 3 of the Guidelines, the Original Award shall be deemed final and effective as of the date of such withdrawal.
Article 7 Appellate Award
The appellate arbitral tribunal may either affirm or modify the Original Award. The award rendered by the appellate arbitral tribunal shall be the final award and be binding upon the parties, in lieu of the Original Award.
Article 8 Allocation of Fees and Costs
The appellate arbitral tribunal shall have the power to decide the allocation of the original arbitration fees and costs, the appellate arbitration fees and costs, the actual expenses, and the reasonable expenses incurred by the parties based on the results of the appellate arbitration and the specific circumstances of the case.
Article 9 Miscellaneous
The relevant provisions of the Arbitration Rules shall apply mutatis mutandis to such procedural matters of appellate arbitration as case acceptance, notice, defence, hearing, mediation and settlement, and award unless they are specifically provided in the Guidelines.
Article 10 Interpretation and Implementation
1. The Guidelines shall be interpreted by the SCIA.
2. The Guidelines shall take effect on 21 February 2019.
SCIA Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules
(Adopted by the Second Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, effective as from February 21, 2019. Amended by the Second Council of SCIA at its eighteenth meeting, such amendments shall
take effect from February 21, 2022.)
MODEL ARBITRATION CLAUSE I
Any dispute arising from or in connection with this contract shall be submitted to the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (the SCIA) for arbitration with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2013) to apply, which shall be administered by the SCIA according to the SCIA Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules.
MODEL ARBITRATION CLAUSE II
Any dispute arising from or in connection with this contract shall be submitted for arbitration in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2013) and the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (the SCIA) shall be the appointing authority.
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules
CONTENTS
Article 1 Purpose
Article 2 Scope of Application
Article 3 Place of Arbitration
Article 4 Administration and Services
Article 5 Request for Arbitration
Article 6 Appointment of Arbitrators
Article 7 Challenge of Arbitrators
Article 8 Charge and Management of Arbitration Fees and Costs
Article 9 Fees of Arbitrators
Article 10 Costs of the Arbitral Tribunal
Article 11 Disclaimer of the SCIA
Article 12 The UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules
Article 13 Interpretation and Implementation
Appendix: Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules
Article 1 Purpose
In order to facilitate the application of the Arbitration Rules of the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (hereinafter the “UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules”) by domestic and foreign parties, in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules and the Arbitration Rules of the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (hereinafter the “SCIA Arbitration Rules”), the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (also known as the South China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission, Greater Bay Area International Arbitration Center, or Shenzhen Arbitration Commission, formerly known as the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission South China Sub-commission and the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission Shenzhen Sub-commission) (hereinafter the “SCIA”) hereby formulates the SCIA Guidelines for the Administration of Arbitration under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (hereinafter the “Guidelines”).
Article 2 Scope of Application
The Guidelines shall apply in any of the following circumstances:
1. Where parties have agreed that disputes between them under Article 2, Paragraph 1(a) or (b) of the SCIA Arbitration Rules shall be submitted to the SCIA in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules.
2. Where parties have agreed to submit disputes to arbitration in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules and the SCIA to perform the administrative functions such as appointing arbitrators.
3. Where the SCIA Arbitration Rules provide for the application of the Guidelines.
Article 3 Place of Arbitration
Where the parties have agreed on the place of arbitration, the parties’ agreement shall prevail. Where the parties have not agreed on the place of arbitration, unless otherwise determined by the arbitral tribunal, the place of arbitration shall be HongKong.
Article 4 Administration and Services
1. The SCIA shall administer the followings:
(a) Appointment of arbitrators;
(b) The decision on the challenge of arbitrators;
(c) Financial management of arbitration cases.
2. The SCIA also provides the following services at the request of the parties or the arbitral tribunal:
(a) Assisting the communication between the arbitral tribunal and the parties as well as between the parties;
(b) Assisting to forward the application of property preservations, etc.;
(c) Providing services for oral hearings, including, but not limited to, providing hearing rooms and audio and/or video recording equipment, arranging interpreters, making records of oral hearings;
(d) Recommending mediation institutions or negotiation facilitation institutions to the parties to facilitate settlement.
Article 5 Request for Arbitration
The claimant shall submit the Request for Arbitration in writing in accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules and pay the registration fee.
Article 6 Appointment of Arbitrators
1. Where the parties have not agreed on the candidate(s) for the arbitral tribunal, or, the candidate(s) for the arbitral tribunal jointly appointed by the parties is/ are unable to carry out his/her duties as an arbitrator and the parties fail to reach an agreement on the replacement of the candidate(s), the SCIA shall carry out the duty as an Appointing Authority under the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules to appoint the arbitrator(s).
2. The party applying for the SCIA’s appointment of arbitrator(s) shall deposit the fees to the SCIA.
Article 7 Challenge of Arbitrators
1. In case of any circumstance stipulated under Article 13(4) of the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules, a party shall submit the application in writing for challenge to the SCIA specifying the basis of the challenge, provide the evidentiary documents and pay the fees in advance to the SCIA for the decision on the challenge.
2. The SCIA shall promptly forward the application for challenge to all the other parties and to each member of the arbitral tribunal who may provide their respective response in writing to the challenge.
3. The President of the SCIA shall make the decision on the challenge.
Article 8 Charge and Management of Arbitration Fees and Costs
1. In accordance with the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules, the arbitration fees and costs charged by the SCIA include:
(a) Registration fee and administrative fees;
(b) Fees and expenses of arbitrators and other necessary costs.
2. The Claimant shall pay a registration fee to the SCIA upon request for arbitration and pay relevant administrative fees in advance.
3. After the arbitral tribunal has been formed, the parties shall pay in advance the fees and expenses of arbitrators and other necessary costs, in accordance with the agreement between the parties and the arbitrator(s) concerned, or under the instruction of the arbitral tribunal.
4. During the course of the arbitration proceedings, if a party fails to pay the relevant fees required, the SCIA shall notify all other parties so that they may pay the fees instead. If such payment is still not made or outstanding, the SCIA may recommend the arbitral tribunal to proceed the arbitration proceedings in a way it deems fit, to suspend or terminate the proceedings.
5. The Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs annexed hereto shall constitute an integral part of the Guidelines.
Article 9 Fees of Arbitrators
Fees of arbitrators shall be negotiated and agreed between the parties and the arbitrators and shall be deposited to the SCIA in accordance with Article 41 of the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules.
Article 10 Costs of the Arbitral Tribunal
The arbitral tribunal shall submit a breakdown of necessary costs to the parties, which shall include but not be limited to, transportation, accommodation and catering costs, with the corresponding receipts or explanation.
Article 11 Disclaimer of the SCIA
The SCIA and its staff shall bear no liabilities for any mistake or negligence by the arbitral tribunal during the course of arbitration proceedings, nor for any award rendered by the arbitral tribunal.
Article 12 The UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules stated in the Guidelines refers to the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2013).
2. Where the parties agree to apply the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (1976) or the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2010), any article in the Guidelines referring to the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2013) shall be regarded as referring to the corresponding article in the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (1976) or UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2010); where there is no corresponding article in the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (1976) or UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2010), the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules (2013) shall apply.
Article 13 Interpretation and Implementation
1. The Guidelines shall be interpreted by the SCIA.
2. The Guidelines shall take effect on 1 December 2016.
Appendix
Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs
1. Registration Fee
The registration fee shall be RMB 5,000 Yuan, which is non- refundable under any circumstance.
2. Administrative Fees
The administrative fees shall include the costs and expenses incurred from providing services under Article 4(1) of the Guidelines in relation to the following:
(1) Appointment of Arbitrators (RMB)
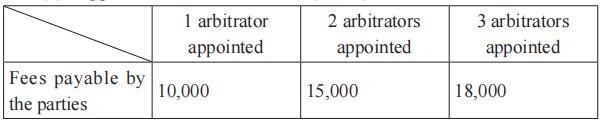
(2) Decision on the Challenge of Arbitrators
An amount of RMB 20,000 Yuan shall be charged for each decision on the challenge of arbitrator(s).
(3) Financial Management Fees of Arbitration Cases
The SCIA shall charge a financial management fee, being 0.1% of the total amount of fees in custody of the SCIA. The minimum financial management fee chargeable shall be RMB 1,000 Yuan, and shall be capped at a maximum of RMB 100,000 Yuan.
(4) Services under Article 4 (2) of the Guidelines
The SCIA shall charge disbursements incurred from services provided by SCIA under Article 4(2) of the Guidelines or from other administrative services requested by the parties or the arbitral tribunal, which shall be charged on actual costs basis.
SCIA Rules of Maritime and Logistics Arbitration
(Adopted by the Second Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, effective as from February 21, 2019. Amended by the Second Council of SCIA at its eighteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from February 21, 2022.)
MODEL ARBITRATION CLAUSE
Any dispute arising from or in connection with this contract shall be submitted to the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (the SCIA) for arbitration in accordance with the SCIA Rules of Maritime and Logistics Arbitration.
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Rules of Maritime and Logistics Arbitration
CONTENTS
Article 1 Qianhai Maritime and Logistics Arbitration Center
Article 2 Jurisdiction
Article 3 Scope of Application
Article 4 Interim Measure(s)
Article 5 Interim Measure(s) Prior to Arbitration
Article 6 Interim Measure(s) during Arbitration
Article 7 Emergency Arbitrator
Article 8 Decision on Interim Measure(s)
Article 9 Change of the Decision on Interim Measure(s)
Article 10 Performance of the Decision on Interim Measure(s)
Article 11 Composition of Arbitral Tribunal
Article 12 Appointment of Arbitrators
Article 13 Defence and Counterclaim
Article 14 Conduct of Arbitration Proceedings
Article 15 Oral Hearing
Article 16 Time Limit for the Final Award
Article 17 Arbitration Fees and Costs
Article 18 Interpretation
Article 19 Implementation
Appendix: Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Rules of Maritime and Logistics Arbitration
Article 1 Qianhai Maritime and Logistics Arbitration Center
The Qianhai Maritime and Logistics Arbitration Center (hereinafter the “SCIA Maritime Arbitration Center”) is established by the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (also known as the South China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission, Greater Bay Area International Arbitration Center, or Shenzhen Arbitration Commission, formerly known as the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission South China Sub-commission, and the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission Shenzhen Sub-commission, hereinafter the “SCIA”) in Shenzhen, China, for the resolution of maritime, logistics and related disputes between the parties.
Article 2 Jurisdiction
The SCIA accepts the following types of arbitration cases in accordance with the agreement between the parties:
1. Disputes related to the transportation of cargo,the transportation of passengers, charter-party, and shipping documents.
2. Disputes related to the sale, construction, reconstruction, repair and charter of, mortgage, security by, management, operations, supply of fuel or personnel to, mariner labour, performance or service(s) provided to any vessel, cruise ship, yacht, aircraft or any other vehicles and ocean facilities of whatsoever kind.
3. Disputes concerning finance, financial lease and insurance issues related to shipping and logistics.
4. Disputes related to maritime and air accidents, including, but not limited to, collision, allision, salvage at sea, casualty, grounding, stranding, fire, explosion, sinking, airplane crashes, ocean and air risks, salvage, obstacle clearance, and general average, etc.
5. Disputes related to ocean exploitation, and the construction, operation, management, maintenance and service of ports, fairway, anchorage,bridge approach, dock, artificial island and airports.
6. Disputes related to ocean and aviation pollution of any kind.
7. Disputes related to the logistics, logistical operations, warehousing, distribution, express service, supply chain, Internet of things (IoT), rail transit, multimodal transport, pipeline transportation, railway and high-speed railway, etc.
8. Disputes related to fishery, aquatic farming and fishing.
9. Any other relevant disputes.
Article 3 Scope of Application
1. As regards the dispute covered by the jurisdiction prescribed in Article 2 hereof:
(a) unless otherwise agreed, the parties shall be deemed to have agreed to arbitration in accordance with these Rules where they have agreed to arbitration by the SCIA Maritime Arbitration Center;
(b) where the parties agree to refer their dispute to arbitration in accordance with these Rules without providing for the name of the specific arbitration institution, they shall be deemed to have agreed to refer the dispute to arbitration by the SCIA under these Rules;
(c) where the parties agree to refer their dispute to the SCIA for arbitration but have not specified for the application of these Rules, the arbitration shall be conducted in accordance with the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
2. Where the parties have agreed to the application of these Rules or the SCIA decides that these Rules shall be applied, any matter not specifically provided for herein shall be subject to the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
Article 4 Interim Measure(s)
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the arbitral tribunal or the emergency arbitrator may grant the interim measure(s) requested by a party in light of the applicable law of the place of arbitration.
2. In light of the applicable law of the place of arbitration, a party may request the SCIA and/or the competent court to take one or more of the interim measures as prescribed below:
(a) the preservation of property;
(b) the preservation of evidence;
(c) to order a party to perform and/or refrain from performing a specific conduct;
(d) any other interim measures provided by law.
3. Where a party requests the competent court to take interim measure(s), it shall not be deemed that it is inconsistent with the arbitration agreement, or that the party has in any way abandoned the arbitration agreement.
Article 5 Interim Measure(s) Prior to Arbitration
1. Before applying for arbitration, a party may request the competent court to take an interim measure(s), or request the SCIA to assist it with requesting the competent court to take an interim measure(s).
2. When requesting the SCIA to provide assistance, the party applying for the interim measures shall provide arbitration agreement and the application for interim measures as prescribed in Article 6, paragraph 1 of these Rules. The SCIA shall forward the documents to the competent court and notify the requesting party when,and whether or not the requested assistance is deemed to be proper after reviewing the documents.
3. The requesting party shall, after the court takes interim measure(s), apply to the SCIA for arbitration within the statutory period as prescribed by the applicable law of the place of arbitration.
Article 6 Interim Measure(s) during Arbitration
1. After the SCIA accepts the case, a party shall, in order for the SCIA to take interim measures, submit an application for interim measures. The application shall clearly set forth the following items:
(a) the names and addresses of the parties;
(b) the basis for taking the interim measures;
(c) the specific interim measures requested;
(d) the place for taking the interim measures and the competent court; and
(e) the relevant legal provisions of the place for taking the interim measures.
2. The SCIA shall forward the application for interim measures to the competent court for the ruling, or submit the application to the arbitral tribunal for the decision, or the emergency arbitrator established under Article 7 hereof for the decision.
Article 7 Emergency Arbitrator
1. The party applying for interim measures after the case is accepted by the SCIA but before the arbitral tribunal is formed may request the SCIA to appoint an emergency arbitrator by submitting an application in writing. The application shall indicate the basis for appointing the emergency arbitrator. Whether the emergency arbitrator is appointed shall be decided by the President of the SCIA.
2.Where the President of the SCIA agrees to appoint the emergency arbitrator, the requesting party shall pay in advance the fee in accordance with these Rules. When the application for appointing an emergency arbitrator is complete, the President of the SCIA shall appoint one (1) arbitrator from the SCIA Panel of Arbitrators within two (2) days to be the emergency arbitrator for disposing of the application for interim measure(s). The SCIA shall notify the parties of the appointment of the emergency arbitrator.
3. The parties may, within two (2) days after the receipt of the notice regarding the appointment of the emergency arbitrator, challenge the arbitrator appointed above, and the President of the SCIA shall make a final decision on the challenge.
4. The emergency arbitrator shall make his/her decision on the application for interim measures pursuant to Article 8 of these Rules.
5. The appointment of the emergency arbitrator shall be terminated on the date when the arbitral tribunal is formed, and shall transfer all of the files to the arbitral tribunal.
6. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the emergency arbitrator shall not act as an arbitrator of the dispute related to the application for interim measures.
7. The procedure prescribed in this Article shall not affect the conduct of any other procedure.
8. Any matter related to the emergency arbitrator appointment shall be governed by the other relevant provisions of these Rules if they are not prescribed herein.
Article 8 Decision on Interim Measure(s)
1. The party requesting interim measure(s) shall satisfy the emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal that:
(a) loss may not be adequately covered by an award of damages if the measure is not ordered, and such possible loss substantially outweighs the harm that is likely to result to the party against whom the measure is directed if the measure is granted; and
(b) there is a reasonable possibility that the requesting party will succeed on the merits of the claim. The determination on this possibility shall not affect the discretion of the arbitral tribunal in making any subsequent determination.
2. The emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal may, before making a decision, require the party requesting an interim measure(s) to provide appropriate security on the basis of the interim measure(s) requested.
3. A decision on the interim measures in accordance with this Article shall be made by the emergency arbitrator within fourteen (14) days upon appointment, or by the arbitral tribunal within fourteen (14) days upon its receipt of the application for interim measures. The emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal shall make a decision on interim measures within ten (10) days upon the date the security is provided pursuant to Paragraph 2 of this Article.
4. The decision on the interim measure(s) shall indicate the basis, be signed by the emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal and affixed with the SCIA’s seal.
5. None of the emergency arbitrator, the arbitral tribunal, the SCIA or its staffs shall be responsible for any loss caused to the parties in the event the emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal decides to take or not to take any requested interim measure.
Article 9 Change of the Decision on Interim Measure(s)
1. The parties may challenge the decision on interim measure(s) by submitting a notice in writing to the SCIA within three (3) days after the party’s receipt of the decision on the interim measure(s), and the SCIA shall forward the notice of challenge to the emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal in order to decide whether to maintain, modify, suspend or terminate the interim measure(s) it has granted. If the appointment of the emergency arbitrator is terminated, the arbitral tribunal formed subsequently shall make the decision on whether to maintain, modify, suspend or terminate the interim measure(s).
2. The emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal may modify, suspend or terminate the interim measure(s) it has granted on its own initiative. The arbitral tribunal may also modify, suspend or terminate the interim measure(s) granted by the emergency arbitrator on its own initiative.
3. The emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal may require any party to promptly disclose any material change in the circumstances that formed the basis on which the interim measure(s) was/ were requested or granted.
4. The party requesting the interim measure(s) may be liable to any party for any cost and damage caused by the measure(s) if the emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal later determines that, in the circumstances then prevailing, the measure(s) should not have been granted. The emergency arbitrator or the arbitral tribunal may award such costs and damages at any time during the proceeding.
Article 10 Performance of the Decision on Interim Measure(s)
The parties shall abide by the decision on interim measure(s) issued by the emergency arbitrator and/or the arbitral tribunal.
Article 11 Composition of Arbitral Tribunal
1. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties or provided by these Rules, an arbitral tribunal shall be composed of three (3) arbitrators.
2. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, within ten (10) days from the date of receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, the Claimant and the Respondent shall each appoint, or entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, an arbitrator, failing which the arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
3. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, within ten (10) days from the date of the Respondent’s receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, the parties shall jointly appoint, or jointly entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, the presiding arbitrator, failing which the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
4. In the alternative, the parties may agree that the presiding arbitrator is to be appointed jointly by the two (2) appointed arbitrators. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, where the two (2) appointed arbitrators fail to appoint the presiding arbitrator within five (5) days from the date of the determination of the second (2nd) arbitrator, the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
5. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the arbitration shall be conducted by a sole arbitrator where the amount in dispute does not exceed RMB 5,000,000 Yuan, or where the parties agree so in writing although the amount in dispute exceeds RMB 5,000,000 Yuan.
6. Where no monetary claim is specified or the amount in dispute is not clear, the SCIA shall determine whether or not to appoint a sole arbitrator after a full consideration of relevant factors, including, but not limited to, the complexity of the case and the interests involved.
Article 12 Appointment of Arbitrators
The SCIA establishes a Panel of Arbitrators. The parties may appoint arbitrators from the Panel, or appoint, either separately or jointly, arbitrators of any nationality from outside the SCIA’s Panel of Arbitrators. The party (or parties) appointing an arbitrator from outside the SCIA’s Panel of Arbitrators shall be confirmed by the President of the SCIA.
Article 13 Defence and Counterclaim
1. The Respondent shall submit its Statement of Defence and evidentiary materials within twenty (20) days of the receipt of the Notice of Arbitration.
2. The Respondent shall submit a counterclaim, if any, in writing within twenty (20) days from the date of receipt of the Notice of Arbitration. The Claimant shall submit its Statement of Defence to the counterclaim in writing within twenty (20) days from the date of receipt of the Notice.
3. If the arbitral tribunal considers there is justified reason(s) for an extension, it may decide to grant an extension of the above time limits. Where the arbitral tribunal has not yet been formed, such decision shall be made by the SCIA.
Article 14 Conduct of Arbitration Proceedings
The arbitral tribunal may conduct the arbitration in the manner it considers appropriate. The arbitral tribunal may decide whether to conduct the arbitration solely on the basis of the written materials and evidence submitted by the parties or to hold an oral hearing.
Article 15 Oral Hearing
1. For a case involving an oral hearing, after the arbitral tribunal has fixed a date and time for the first oral hearing, the parties shall be notified at least ten (10) days prior to the oral hearing. A party having justified reason(s) may request a postponement of the oral hearing. However, such request shall be communicated in writing to the arbitral tribunal at least seven (7) days prior to the scheduled date of the oral hearing. The arbitral tribunal shall decide whether or not to postpone the oral hearing.
2. Where a party has justified the reasons for its failure to submit a request for a postponement of the oral hearing within the time period specified in Paragraph 1 of this Article, the arbitral tribunal shall decide whether or not to postpone the oral hearing.
3. A notice regarding the date and time of a subsequent oral hearing, as well as a notice regarding the date and time of a postponed oral hearing, shall not be subject to the time limit specified in Paragraph 1 of this Article.
Article 16 Time Limit for the Final Award
1. The arbitral tribunal shall render its arbitration award within three (3) months from the date on which the arbitral tribunal is formed.
2. Upon the request of the arbitral tribunal, the President of the SCIA may extend the time limit if he/she considers it necessary and the reasons for the extension are deemed justified.
3. The following period shall be excluded when calculating the time limit in the preceding Paragraphs:
(a) tperiod for appointing experts for, inter alia, appraisal, audit, evaluation, testing, expert consultancy pursuant to the SCIA Arbitration Rules;
(b) tperiod for mediation pursuant to the SCIA Arbitration Rules;
(c) tperiod of suspension pursuant to the relevant law, these Rules or the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
Article 17 Arbitration Fees and Costs
1. The parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in accordance with the applicable provisions in the Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration.
2. The Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration attached hereto shall constitute an integral part of these Rules.
Article 18 Interpretation
1. The headings of the articles in these Rules shall not be construed as interpretations of the meanings of the provisions contained therein.
2. These Rules shall be interpreted by the SCIA.
Article 19 Implementation
These Rules shall be effective as from 21 February 2019.
Appendix
Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration
Article 1 Registration Fee
A registration fee of RMB 5,000 Yuan shall be payable upon application for arbitration, for the purposes of examining the application for arbitration, initiating the arbitration proceedings, computerizing management, filing management and correspondence. The registration fee is non- refundable.
Article 2 Schedule of Arbitration Fees and Costs
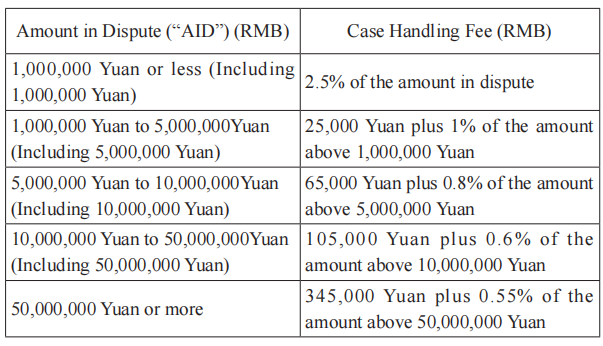
1. The parties shall pay the arbitration fees and costs in advance in accordance with the rates under this Schedule above for their respective claim or counterclaim. The AID referred to in this Schedule shall be on the basis of the amount of money claimed by the parties. Where no monetary claim is specified or the amount in dispute is not clear, the amount of arbitration fee shall be determined by the SCIA in consideration of the specific rights and interests involved in the disputes.
2. If the arbitration fee is charged in a foreign currency, an amount of the foreign currency equivalent to the corresponding RMB value specified in this schedule shall be paid.
3. The SCIA may charge for other disbursements reasonably incurred in accordance with the relevant provisions under the SCIA Rules.
4. Unless otherwise stipulated by the SCIA Arbitration Rules and agreed by all the parties, the remuneration of the arbitrator(s) shall be decided by the SCIA and shall be payable by the SCIA out of the arbitration fees and costs collected by the SCIA under this Schedule. While determining the remuneration of the arbitrator(s), the SCIA shall take into account of factors such as the time spent by the arbitrator(s) to handle the case, the AID the complexity of the case, and the due diligence and efficiency of the arbitrator(s). The personal fee rate of any arbitrator (if any) shall only be for SCIA’s reference, and is not binding on the SCIA.
Article 3 Miscellaneous
Other fees and costs, including, but not limited to, the appointment fee for an emergency arbitrator, shall be governed by the SCIA Arbitration Rules if there are no provisions stipulated under these Rules.
SCIA Online Arbitration Rules
(Adopted by the Second Council of SCIA at its seventh meeting, effective as from February 21, 2019. Amended by the Second Council of SCIA at its eighteenth meeting, such amendments shall take effect from February 21, 2022.)
MODEL ARBITRATION CLAUSE
Any dispute arising from or in connection with this Contract shall be submitted to Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (the SCIA) for online arbitration. The Parties hereby agree that the arbitration documents shall be delivered to the following electronic addresses:
Party A’s E-Mail: Mobile Phone No.:
Party B’s E-Mail: Mobile Phone No.:
Party C’s E-Mail: Mobile Phone No.:
When a Party changes its e-mail address or mobile phone number, it shall immediately give a written notice to other Parties.
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Online Arbitration Rules
CONTENTS
CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1 Purpose
Article 2 Definitions
Article 3 Scope of Application
Article 4 Data Storage and Usage
Article 5 Requirements for Online Arbitration
Article 6 Hearing of Online Arbitration
Article 7 Identity Verification and Signature
CHAPTER II SUBMISSION AND SERVICE OF DOCUMENTS
Article 8 Submission of Documents
Article 9 Electronic Service Address
Article 10 Electronic Service
CHAPTER III EVIDENCE
Article 11 Submission of Evidence
Article 12 Collection of Evidence
Article 13 Review of Electronic Data
CHAPTER IV ARBITRATION PROCEEDINGS
Article 14 Request for Arbitration
Article 15 Acceptance of a Case
Article 16 Notice of Arbitration
Article 17 Statement of Defence
Article 18 Amendments to the Claim
Article 19 Counterclaim
Article 20 Objection to Jurisdiction
Article 21 Formation of Arbitral Tribunal
Article 22 Challenge of Arbitrators
Article 23 Hearings
Article 24 Record of Hearings
Article 25 Time-limit for the Arbitral Award
Article 26 Arbitral Documents
Article 27 Electronic Archival Files
Article 28 Change of Procedure
CHAPTER V MISCELLANEOUS
Article 29 Limitation of Liabilities
Article 30 Interpretation of these Rules
Article 31 Coming into Force
Appendix: Schedule of Online Arbitration Fees
Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration Online Arbitration Rules
CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1 Purpose
These Rules are formulated by the Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration (also known as the South China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission, Greater Bay Area International Arbitration Center, or Shenzhen Arbitration Commission, formerly known as the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission South China Sub-commission, and the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission Shenzhen Sub-commission) (hereinafter the “SCIA”) in accordance with the SCIA Arbitration Rules to resolve commercial disputes between equal parties through impartial and efficient online arbitration.
Article 2 Definitions
1. “Online arbitration” refers to a dispute resolution method of conducting arbitration by use of the Internet or other information technologies.
2. “Online Arbitration Service Platform” refers to a dedicated platform for the SCIA to handle arbitration cases and for the parties to conduct arbitral activities.
3. “Electronic data” refers to information generated from e-mail, electronic data exchange, online chat record, blog, microblog, instant message, text message, electronic signature, domain name, or information stored in an electronic medium.
4. “Online video hearing” means hearings held through online video or other forms of electronic communication.
Article 3 Scope of Application
1. For disputes arising from online transactions or other commercial disputes, where the parties agree to submit their dispute to the SCIA for online arbitration (also known as Internet arbitration, electronic arbitration, network arbitration, and other similar names), the parties shall be deemed to have agreed to arbitration by the SCIA in accordance with these Rules.
2. Any matter not covered by these Rules shall be governed by the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
Article 4 Data Storage and Usage
The Online Arbitration Service Platform shall store and use dispute-related data in compliance with the provisions of the Cybersecurity Law of the People’s Republic of China and other applicable laws and regulations.
Article 5 Requirements for Online Arbitration
Parties who have agreed to conduct online arbitration are required to possess the equipment and technical capacity necessary for online arbitration,including but not limited to the ability to use e-mailand other electronic communication tools and to participate in online video hearings; failing which, the SCIA may decide to accept and handle the case in accordance with the SCIA Arbitration Rules.
Article 6 Hearing of Online Arbitration
Online arbitration cases shall be heard online. Case acceptance, payment of fees and costs, service, exchange of evidence, hearing, mediation,rendering of an award, and other procedures related to online arbitration cases shall in general be conducted online.
Article 7 Identity Verification and Signature
1. Where the parties participate in arbitration through the Online Arbitration Service Platform, they shall complete the identification procedure through such online approaches as identification and/ or license checks, biometric identification, or certification by a national unified identity platform, and obtain a dedicated account for logging into the Online Arbitration Service Platform.
2. Any act performed on the Online Arbitration Service Platform by login with a dedicated account shall be deemed as an act of the person having been identified, unless it is caused by a technology induced-system error of the Online Arbitration Service Platform or the person having been identified can prove that its account for Online Arbitration Service Platform has been used without authorization.
3. For any case heard by an arbitral tribunal online, where the arbitrators, the parties, and other persons related to the arbitration have confirmed a mediation agreement, a transcript or other arbitral materials through online confirmation, electronic signature or other online methods, the corresponding “signature” requirements shall be deemed to be satisfied.
CHAPTER II SUBMISSION AND SERVICE OF DOCUMENTS
Article 8 Submission of Documents
1. The parties shall present their evidence by uploading and importing the online electronic data into the Online Arbitration Service Platform, or by uploading offline evidence to the platform after converting it to electronic format through scanning, photographing, transcription, or other means.
2. The time of submission of a document shall be deemed as the time the document is successfully uploaded to the Online Arbitration Service Platform.
3. Each party shall retain a copy of any submitted electronic document and its upload record, to evidence the facts and circumstances regarding the submission of relevant documents for examination by the other party and the arbitral tribunal.
Article 9 Electronic Service Address
1. The parties shall agree in the arbitration agreement or contract on one or a combination of, for example, the Online Arbitration Service Platform, phone number, facsimile number, e-mail, or instant messaging account as their electronic service address(es), failing which they may agree on such address(es) through a supplemental agreement.
2. The parties shall confirm their electronic service address(es) to the SCIA when applying for arbitration or submitting a defence.
3. Where the parties have neither agreed on nor confirmed to the SCIA their electronic service address(es), the phone number, facsimile number, e-mail, instant messaging account, or other contact information they have used in the electronic transaction or provided during web registration may be deemed as their electronic service address(es).
4. Any party that changes its electronic service address(es) during the online arbitration proceedings shall notify the SCIA in time.
5. The parties shall ensure that their agreed or confirmed electronic service addresses are lawful and valid, and solely bear the risk of service failure due to, for example, erroneous address or legal restrictions imposed by the place of arbitration.
Article 10 Electronic Service
1. The SCIA may serve relevant documents through one or a combination of, inter alia, the Online Arbitration Service Platform, text message, facsimile, e-mail, or instant message.
2. Any arbitral document sent by the SCIA to a party shall be deemed to have been duly served if:
(a) the document has been sent to the electronic service address agreed upon by the party;
(b) the SCIA sends a notice to the party to check or download the document at the Online Arbitration Service Platform;
(c) the addressee replies that it has received the served materials or it has performed relevant arbitration conducts in accordance with the served materials; or
(d) the addressee’s system indicates that the addressee has read the served materials, or other evidence demonstrates that the addressee has received the served materials.
3. (a) The date on which a document is successfully sent as indicated by the network system shall be deemed as the date of service;
(b) Notwithstanding the foregoing, if the addressee establishes that the date such document reaches its specified system is inconsistent with the date of successful sending indicated by the corresponding SCIA system, the date established by the addressee shall prevail.
CHAPTER III EVIDENCE
Article 11 Submission of Evidence
The parties shall submit their evidence through the Online Arbitration Service Platform or other methods recognised by the SCIA.
Article 12 Collection of Evidence
1. An arbitral tribunal may contact, inter alia, network service providers, logistics and delivery companies, third-party payment platforms, and providers of electronic certification service or electronic evidence preservation service to investigate the facts and collect evidence with respect to the issues involved in a case.
2. Any evidence gathered by the arbitral tribunal shall be submitted to the parties for examination and comments.
Article 13 Review of Electronic Data
1. An arbitral tribunal may, in consideration of the results of examination of evidence, review and judge the authenticity of the generation, collection, storage and transmission of the electronic data, with particular focus on:
(a) whether the computer systems and other hardware and software environment relied on for the generation, collection, storage, and transmission of the electronic data are secure and reliable;
(b) whether the electronic data have a clear generator and time of generation, and whether the electronic data present clear, objective, and accurate information;
(c) whether the electronic data have a clear storage and safekeeping medium and have been kept safe by appropriate means and methods;
(d) whether the entities, tools, and methods that extract and preserve the electronic data are reliable and whether the extraction process can be reproduced;
(e) whether the electronic data are incomplete or have been altered due to addition, deletion, or modification of information; and
(f) whether the electronic data may be verified through a specified form.
2. The arbitral tribunal shall confirm a party’s electronic data if they can be established as authentic by electronic signature, credible time-stamp, hash value verification, blockchain or other means of evidence collection, technological methods of preservation and anti-tampering, or by certification from an electronic evidence collection and storage platform.
3. The parties may request to have persons with special knowledge to comment on the technical issues of electronic data. The arbitral tribunal may, based on such request or its powers, engage third parties to verify the authenticity of the electronic data or gather other related evidence for cross-check.
4. Any electronic version of the identity document, duplicate business license, letter of authorization, identity document of legal representative, and other certification materials, as well as any electronic version of documentary evidence, expert opinion, record of on-site investigation, and other evidentiary materials submitted by a party, after passing the review of the arbitral tribunal, shall be deemed as an original document for purposes of formality requirement. If the other party objects to the authenticity of any of the foregoing materials with due cause, the arbitral tribunal may require the the party to provide the original document.
CHAPTER IV ARBITRATION PROCEEDINGS
Article 14 Request for Arbitration
A party applying for arbitration shall submit a Request for Arbitration, evidentiary materials, and its certificate of qualification through the Online Arbitration Service Platform.
Article 15 Acceptance of a Case
After the Claimant submits a Request for Arbitration and evidentiary materials, and makes advance payment of arbitration fees, the SCIA shall accept the case if it finds the required formalities complete.
Otherwise, the SCIA may request the Claimant to complete them within a specified time period. If the formalities remain incomplete upon the expiry of the specified time period, it shall be deemed that no request for arbitration has been made.
Article 16 Notice of Arbitration
After the SCIA accepts the Request for Arbitration, the SCIA shall send a Notice of Arbitration to the parties together with one copy of each of these Rules, the SCIA Arbitration Rules, the SCIA Panel of Arbitrators, and the Request for Arbitration and its attachments submitted by the Claimant shall be forwarded to the Respondent simultaneously.
Article 17 Statement of Defence
The Respondent shall submit the Statement of Defence, opinion on evidence, and the evidentiary materials it has relied on through the Online Arbitration Service Platform within five (5) days from receipt of the Notice of Arbitration.
Article 18 Amendments to the Claim
A party that applies to amend its claim shall submit its amendment through the Online Arbitration Service Platform within five (5) days from receipt of the Notice of Arbitration. Whether a late application will be accepted shall be at the discretion of the SCIA or arbitral tribunal.
Article 19 Counterclaim
1. A Respondent that applies to file a counterclaim shall submit its counterclaim through the Online Arbitration Service Platform within five (5) days from receipt of the Notice of Arbitration. Whether a late application will be accepted shall be at the discretion of the SCIA or arbitral tribunal.
2. The provisions of Articles 14-18 of these Rules shall apply mutatis mutandis to the submission, acceptance, and service of, and defence and amendments to, the counterclaim.
Article 20 Objection to Jurisdiction
Any objection to the existence or validity of an arbitration agreement or to jurisdiction shall be raised through the Online Arbitration Service Platform before the expiry of the time-limit for the submission of the first defence.
Article 21 Formation of Arbitral Tribunal
1. An arbitral tribunal is composed of a sole arbitrator. An arbitral tribunal may be composed of three (3) arbitrators in special circumstances or as agreed by the parties.
2. Where an arbitral tribunal is composed of a sole arbitrator, the parties shall jointly appoint, or entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, the arbitrator within five (5) days from the Respondent’s receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, failing which, the arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
3. Where an arbitral tribunal is composed of three (3) arbitrators, the parties shall each appoint, or entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, one arbitrator within five (5) days from their respective receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, and jointly appoint, or entrust the President of the SCIA to appoint, the presiding arbitrator within five (5) days from the Respondent’s receipt of the Notice of Arbitration, failing which, the presiding arbitrator shall be appointed by the President of the SCIA.
Article 22 Challenge of Arbitrators
A party wishing to challenge an arbitrator on the grounds of the information disclosed by the arbitratorshall put forward the challenge within three (3) days from receipt of such information.
Article 23 Hearings
1. In principle, an arbitral tribunalshall not hold hearings for online arbitration cases.
2. An arbitral tribunal may, however, where it deems it necessary, hear a case through online video hearings, online exchange of information, teleconferences, and other appropriate means, or may decide to hold offline hearings while the other processes are still conducted online.
3. For any case heard under Paragraph 2 of this Article, the parties shall be notified of the date of hearing no later than five (5) day in advance.
Article 24 Record of Hearings
An arbitral tribunal may create a record of oral hearings during mediation, exchange of evidence, hearing, deliberation, and other arbitration proceedings for a case heard online simultaneous with voice recognition technologies or by manual work. A record of oral hearings, once verified and confirmed online, shall have the same legal force as a written record.
Article 25 Time-limit for the Arbitral Award
An arbitral tribunal shall render an arbitral award within one (1) month from its formation. Where there are special circumstances or legitimate reasons justifying an extension of the duration of the arbitration, the SCIA may approve an appropriate extension upon the request of the arbitral tribunal.
Article 26 Arbitral Documents
Arbitral documents, including the arbitral award, mediation statement and decision on dismissal, shall be signed by the arbitrator(s) electronically and affixed with the electronic seal of the SCIA.
Article 27 Electronic Archival Files
The SCIA shall use the Online Arbitration Service Platform to generate electronic files simultaneously with the case and, create an electronic archive. Where a paper archive for a case has been fully converted into an electronic archive, the electronic archive shall replace the paper dossier.
Article 28 Change of Procedure
During an online arbitration, the SCIA may, upon the request of any party or as deemed necessary by the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal, change some or all of the procedures of the arbitration into the procedures stipulated in the SCIA Arbitration Rules in view of the circumstances of the case in question.
CHAPTER V MISCELLANEOUS
Article 29 Limitation of Liabilities
Arbitrators,the SCIA and its related persons shall bear no civil liability to any person for any loss from force majeure, computer viruses, cyberattacks, system instability, network faults, or other circumstances not intentionally caused by the SCIA or the arbitral tribunal.
Article 30 Interpretation of these Rules
1. The headings of the articles in these Rules shall not be construed as an interpretation for the provisions thereunder.
2. The SCIA reserves the right to interpret these Rules.
Article 31 Coming into Force
These Rules shall be effective as from 21 February 2019.
Appendix
Schedule of Online Arbitration Fees
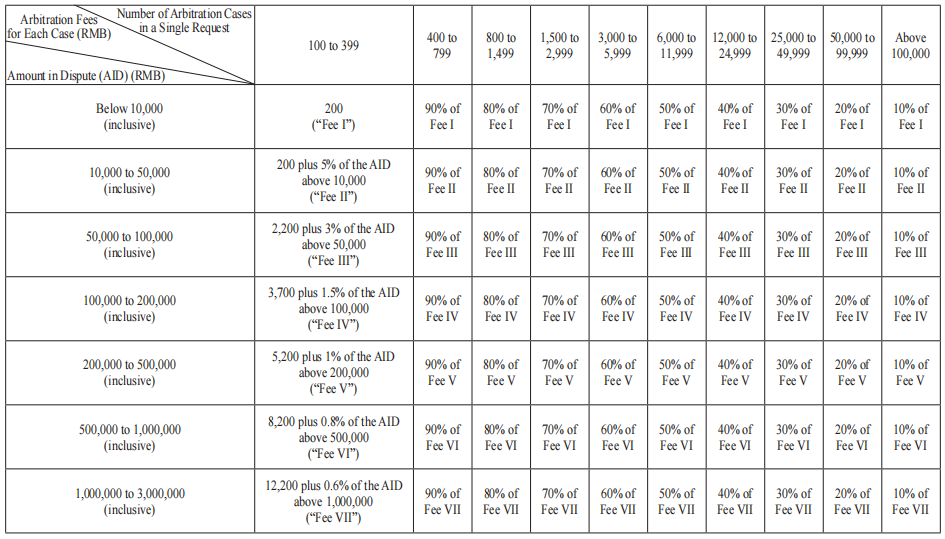
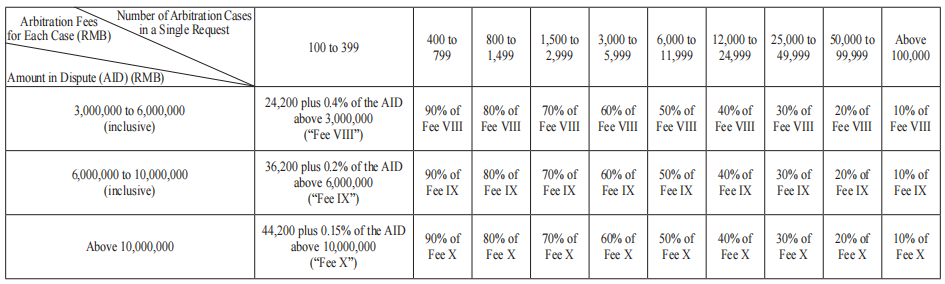
1. This Schedule applies to Chinese Mainland disputes, international or foreign-related disputes, and disputes related to the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, the Macao Special Administrative Region and Taiwan Region.
2. This Schedule shall apply to cases where all proceedings are conducted online, excluding cases where only parts of proceedings are conducted online.
3. The AID referred to in this Schedule shall be based on the amount claimed by the parties. Where no monetary claim is specified or the amount in dispute is not clear, the amount of arbitration fees shall be determined by the SCIA in consideration of the specific rights and interests involved in the disputes.
4. The Number of Arbitration Cases in a Single Request referred to in this Schedule shall be based on the number of arbitration cases requested online by the parties in the same series. For the cases requested in the same series, if the number is between 1 and 9, the arbitration fees for each case shall be calculated according to the Schedule II attached to the Arbitration Rules; if the number is between 10 and 99 and the facts of the cases are similar, the arbitration fees for each case shall be at 50% of the amount calculated according to Schedule II; if the number of cases requested in the same series is more than 100 and the facts of the cases are similar, the arbitration fees for each case shall be calculated based on the corresponding range of the AID for each case and the corresponding range where the total number of the cases requested in the same series fits. The rate of arbitration fees for claims applies to counterclaims in the same online arbitration case.
5. If the arbitration fee is charged in a foreign currency, an amount of foreign currency equivalent to the corresponding RMB value specified in this Schedule shall be paid.
6. Where the arbitration proceeding is changed from the online arbitration proceeding to any other arbitration proceeding provided in the Arbitration Rules, the arbitration fees shall be calculated by the SCIA in accordance with the Schedule of Fees and Costs of Arbitration attached to the Arbitration Rules. The arbitration fees advanced by the parties shall be used to offset the arbitration fees payable for the changed proceeding, and the arbitration fees shall be paid by the parties in full prior to the first oral hearing.
7. This Schedule shall be effective as from 21 February 2019. The old Schedule of Online Arbitration Fees effected from 15 August 2017 is expired at the same time.

